A healthy heart is a miracle of efficiency. The regular muscular contraction of its four cavities pumps about 5 liters of blood through the body every minute. Each detected heartbeat consists of two beats, the first being the beat of the upper cavities, i.e., vestibules (or atria), and other lower cavities, i.e., ventricles (or ventricles). The contraction is triggered by electrical impulses generated in the sinus node, a group of specialized cells in the right atrium.
CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS: General | Symptoms | Natural Stimulant | Left Lobby | Causes | Diagnostic Procedures | Treatment | Prevention | Questions and Answers | Sources/references
A disturbance in the regular heartbeat pattern is called an arrhythmia or heart rhythm disorder. Almost everyone experiences some arrhythmia occasionally, usually in the form of mild palpitations or a "skipped" pulse. (What we feel as a missed beat is a premature beat that is too weak to be felt, followed by a one- or two-second pause, followed by a relatively strong beat; the pause between the two beats is perceived as a missed beat.) Mild, isolated disturbances, these species are usually not dangerous. A doctor should define recurring arrhythmias.
There are two main groups of arrhythmias: tachycardia, which means the heart beats too fast, and bradycardia, which means the heart beats too slow. (Both refer only to abnormal ups or downs in heart rate, not regular daily changes depending on whether you're active or resting.) A resting heart rate is somewhere between 60 and 100 beats per minute. Tachycardia means that the frequency is more than 100 beats per minute, and bradycardia means that the frequency is less than 60 beats per minute. Both can occur in attacks or as a constant condition.
Figure: There are two main groups of arrhythmias.
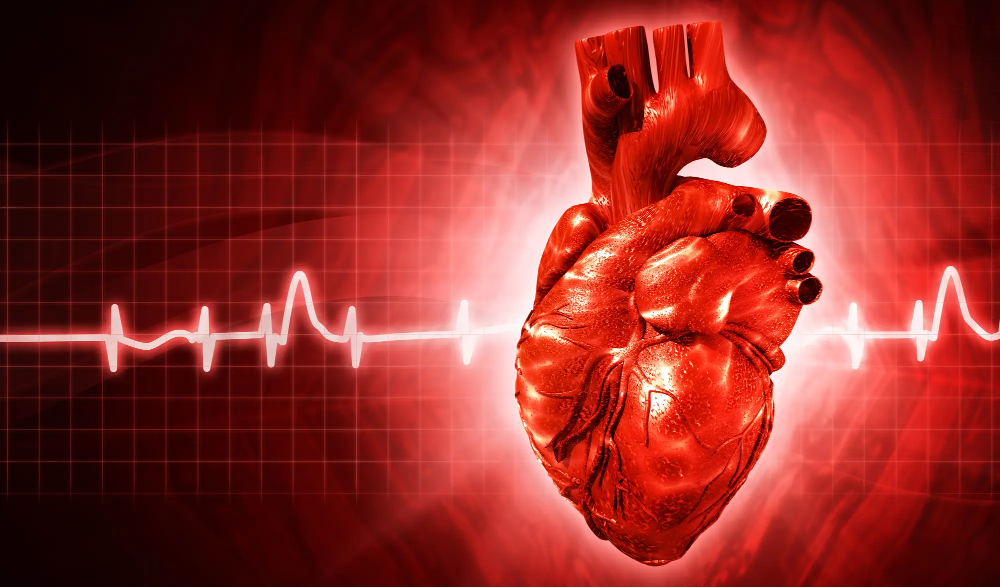
Most arrhythmias belong to the group of tachycardias. Some originate in lobbies, others in hallways. Ventricular arrhythmias are much more dangerous. Most cases of sudden cardiac death are caused by ventricular arrhythmias, not heart attacks, as was once thought. Particularly dangerous is ventricular fibrillation (ventricular fibrillation), in which the function of the ventricles is so uncoordinated that they only flutter and do not pump blood. If not interrupted, it causes death within minutes.
Video content: When is heart arrhythmia dangerous?

Bradycardia can be caused by damage to the nerves that control the heartbeat, damage to the sinus node, where the heart's electrical potentials are generated, or damage to the transmission of stimuli through the heart. In the latter defect, known as heart block, electrical impulses from the atria are not transmitted to the ventricles due to a defect in the conduction system. Stimuli can be blocked intermittently or permanently. In the worst case, such a disorder can cause death.
Symptoms
Occasional, isolated heart rhythm disturbances are common and usually not dangerous. The signs of more dangerous arrhythmias are:
For tachycardia, i.e., abnormally fast heartbeat:
- repetitive vibrations; they are defined as an unpleasant awareness of the heartbeat - you can feel them as a strong pulse in the neck or pounding in the chest
- chest pain, nausea, fainting, sweating, shortness of breath, confusion or dizziness
For bradycardia, i.e., abnormally slow heartbeat:
- Tiredness, shortness of breath, dizziness, or loss of consciousness
Consult your doctor if:
- Feel an irregular heartbeat that repeats or makes you uncomfortable - any prolonged or very irregular arrhythmia should be investigated and its danger determined.
- When taking medication for one type of arrhythmia, you notice a new pattern of heart rhythm disturbance - some antiarrhythmic drugs can worsen heart rhythm disturbances.
- You have side effects when taking antiarrhythmic drugs, such as dizziness, vomiting, nausea, blurred vision, ringing in the ears, diarrhea, loss of gait, or loss of consciousness - by changing the drug, the problems may disappear.
Natural booster
The heartbeat begins with electrical impulses in the sinus node, a group of cells in the right atrium. Impulses are transmitted along several paths through the gums and left atrium and cause atrial contraction. They then continue their journey toward the ventricles, partially slowing down in the atrioventricular node. The ventricles contract just behind the atria. Coordinated contraction of the heart ensures efficient blood flow.
Left vestibule
The left atrium is one of the four chambers of the human heart and plays a vital role in the cardiovascular system. The left atrium is located in the lower left part of the heart, just below the left atrium and to the left of the right atrium. The primary role of the left atrium is to pump oxygenated blood into the body. When it contracts, it pushes blood into the aorta, the central and largest artery in the human body, which then distributes oxygen-rich blood to all body parts.
Image: The primary role of the left atrium is to pump oxygenated blood into the body.
.jpeg)
The left atrium is vital for survival, and its dysfunction can lead to various health conditions. For example, left atrial hypertrophy (LVH) is a condition in which the muscular wall of the left ventricle thickens. Heart failure can also originate from the left ventricle when it weakens and cannot pump blood efficiently. In the context of heart health and cardiovascular disease, the function and health of the left atrium is often a central topic, given its essential role in supplying the body with oxygen-enriched blood.
Causes
Any condition that affects the structure of the heart muscle or heart valves or changes the heart's electrical activity can alter the regular heartbeat. Many heart diseases cause arrhythmias. A common trigger is severe coronary heart disease; scars forming in the heart muscle can interfere with transmitting electrical impulses. Other causes are:
- congenital heart defects,
- diseases of the heart muscle,
- heart valve defects,
- and other diseases, e.g., lung diseases or increased thyroid function.
External forces, such as an electric current or a severe chest injury, can also trigger them. Ventricular arrhythmias are most often caused by heart disease and are a known complication of a heart attack. Atrial arrhythmias are also associated with heart disease, but other causes are familiar, or no cause can be found. Atrial flutter (atrial fibrillation) is often associated with high blood pressure. Many bradycardias are associated with heart blocks.
Arrhythmias can also be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system (which controls all involuntary bodily functions, including heart rate). Effective control of the autonomic nervous system is based on a good balance between the sympathetic nervous system, which accelerates bodily functions, and the parasympathetic nervous system, which inhibits bodily functions. Sometimes, a stroke disrupts this balance, which can result in arrhythmia.
Video content: Arrhythmias | Types, pathophysiology, diagnosis, Treatment.

A heart rhythm disorder can also be caused by rapidly injecting certain chemicals or hormones into the bloodstream. Drugs such as caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, and cocaine increase heart rate and cause other heart rhythm abnormalities, as does inhalation of aerosol propellants. The same happens when adrenaline is released, e.g., in shock, fear, and anxiety.
Diagnostic procedures
Arrhythmia is most accurately defined with an ECG recording of the heart's electrical activity. However, an EKG is only valid if an arrhythmia occurs during the recording, which does not happen often. To detect arrhythmia, we can examine it with a Holter monitor, a portable device that records the electrical activity of the heart 24 hours a day. The diagnosis is made more accessible with tests that trigger the arrhythmia. Walking on the conveyor belt can, e.g., trigger a disorder that occurs during physical exertion.
Electrophysiological testing may also be helpful. Small electrode catheters, introduced through a vein or artery to different heart parts, record the transmission of electrical stimuli. An "electrical map" of the readings shows the signals' position, direction, and speed so doctors can determine where the problem is coming from or where stimuli are not being translated.
Treatment
After identifying the arrhythmia, the doctor determines whether you need Treatment, with drugs or surgery. The treatment decision is based not only on the type of arrhythmia but also on the patient's age, physical fitness, and information on previous heart diseases.
Conventional medicine
For mild disorders, the doctor will suggest some measures you can take yourself at home (see Treatment at Home). If necessary, he will prescribe medication. He will choose them according to the type of arrhythmia, previous diseases, and other heart diseases' simultaneous presence.
Drugs defined as antiarrhythmics — including quinidine, amiodarone, and digitalis preparations — are very potent and can cause serious side effects, so they are not routinely prescribed. Electrophysiological testing is prescribed several times at the same time to determine whether the drugs will be effective and will not cause side effects.
Image: Sometimes, a more invasive treatment is required.
.jpg)
In emergencies, an electric shock is often used, interrupting the arrhythmia and restoring the normal rhythm; then, the patients are given the medicine. They also treat with electric shock when the drugs are ineffective or if the doctor expects an emergency due to accompanying heart diseases.
Some patients have a device implanted in their body, which enables long-term control of heart rhythm disorders. People with symptomatic bradycardia (they feel symptoms when they have bradycardia) are usually implanted with a pacemaker.
Patients prone to ventricular fibrillation can be given a cardioverter-defibrillator, a device that delivers an electric shock through electrodes in the heart when needed. Patients with bradycardia and tachycardia may be implanted with a pacemaker defibrillator. This device can restore a normal heartbeat with an electric shock while maintaining an average, regular rate.
Sometimes, a more invasive treatment is required. Suppose a limited area of the heart muscle causes the arrhythmia. In that case, they can use a technique known as catheter ablation: radio waves from a device inserted through a vein or artery damage that piece of tissue, turning it off. In rare cases, open heart surgery is required to remove the tissue.
Alternative ways
You should consult a cardiologist for emergency treatment and long-term prevention of serious arrhythmias. Alternative treatment methods can complement, but should not replace, standard heart disease treatment. Alternative treatments may reduce the need for antiarrhythmic drugs. For mild arrhythmias, alternative treatment methods may be sufficient.
Aromatherapy
Mild arrhythmia can be calmed down with lemon oil added to the bath. Also, try a few drops of orange blossom oil, called neroli oil.
Chinese herbs
Many Chinese herbs can ease the symptoms of arrhythmias. Some — e.g., ephedra (Ephedra sinica) — can worsen the condition. Consult a Chinese herbalist, and tell your doctor if you take any herbs for other problems.
Herbs
Many herbs contain active ingredients that strengthen and calm the heartbeat. Some, e.g., foxglove (Digitalis purpurea), are too potent for laypeople. Hawthorn (Crataegus laevigata), a mild but effective herb for treating heart disease, is best suited for home use. Hawthorn dilates blood vessels and stimulates the heart muscle, which helps to calm arrhythmias. Soak 2 to 3 tablespoons of herbs in hot water; drink four cups daily.
Homeopathy
Homeopathic medicine offers medicines for the immediate and long-term Treatment of mild arrhythmias. Lachesis, digitalis and aconitum are used to calm palpitations. Consult a homeopathy specialist about dosages.
Way of life
The heart rate increases During physical exercise, but it settles at a lower level after exercise. People who do not exercise have a heart rate of around 80 beats per minute, while those who exercise regularly have a heart rate of between 60 and 65 beats per minute.
Video content: Here are ways to get your heart back on track.

Physical activity also eliminates excess adrenaline, a hormone that stimulates the heart and the whole body. In susceptible people, arrhythmias can be caused by nicotine from cigarettes. If you have been diagnosed with arrhythmia and you smoke, stop.
Medicine of mind and body
Relaxation techniques reduce stress, which increases heart rate and can trigger some heart rhythm disorders. You can relax with various activities, from exercise to meditation and yoga. Find the one that works best for you and stick with it; the benefits of relaxation become apparent only after a more extended period.
Nutrition
The minerals calcium, magnesium, and potassium play an essential role in regulating cardiac activity. Lack of these minerals can cause arrhythmias. (Excessive concentration can also be dangerous, especially with calcium.) Intravenous magnesium calms tachycardia and other arrhythmias.
Image: Electrolytes play an essential role in regulating cardiac activity.
.jpg)
Magnesium is found in nuts, legumes, soybeans, bran, dark green vegetables, and fish. The source of potassium is fruits and vegetables. You can also use your potassium and magnesium stores if you overeat salt or saturated fat or abuse diuretics or laxatives.
Home remedies
- The best method to stop a tachycardia attack is to rest. Take a deep breath and relax.
- A tachycardia attack can also be interrupted by applying light pressure to the carotid artery on the right side of the neck. Let your doctor show you where and how to press.
- For atrial arrhythmias, try t. i. "vagal maneuvers". Sit, bend forward at the waist, then hold your breath and tense up as if you were blowing up a balloon. By doing this, you shift control of bodily functions from the sympathetic nervous system, which speeds them up, to the parasympathetic, which slows them down.
A splash of water on the face
Have you ever wondered how sea lions survive the shock of jumping into cold water? Like other mammals, they are protected by an automatic nervous response that slows the heart rate. We humans have this answer, too, which can help if you suffer from occasional bouts of tachycardia. The next time you have an attack, try immersing your face in cold water. The heart rate will decrease momentarily, which may stop the tachycardia attack.
Prevention
Limit caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, and other stimulants, which can increase your heart rate. If you have already had tachycardia, give up these substances altogether. Reduce stress through sports, meditation, or whatever works for you. If you have heart disease, make the right treatment decisions; this will prevent or control arrhythmias.
Questions and answers
Is heart arrhythmia always dangerous?
Occasional, isolated heart rhythm disturbances are common and usually not dangerous.
Can arrhythmia be cured?
Treatment of cardiac arrhythmia with radiofrequency ablation has a 95-98% chance of cure. Taking lifelong medication will no longer be necessary. However, the treatment process varies depending on the symptoms, the disease type, and the specialist's evaluation [1].
Can we have arrhythmia and not realize it?
Cardiac arrhythmias may not cause any signs or symptoms. Your doctor may notice an irregular heartbeat when examining you for another medical reason[2].
What happens if heart arrhythmia is not treated?
Complications depend on the type of arrhythmia. In general, complications of cardiac arrhythmias can include stroke, sudden death, and heart failure. Cardiac arrhythmias are associated with an increased risk of blood clots. If the clot breaks loose, it can travel from the heart to the brain and cause a stroke[2].
How can we prevent the occurrence of arrhythmia?
Limit caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, and other stimulants, which can increase your heart rate. If you have already had tachycardia, give up these substances altogether. Reduce stress through sports, meditation, or whatever works for you. If you have heart disease, make the right treatment decisions; this will prevent or control arrhythmias.
Sources and references
Source: Family Health Guide. Conventional and alternative Treatment, Dr. Jaro Lajovic, Publishing House Mladinska knjiga
- Heart Arrhythmia can be cured – Don't ignore it, it can become fatal - https://www.vejthani.com.
- Heart arrhythmia - https://www.mayoclinic.org











 Facebook
Facebook
 Instagram
Instagram
 info@moja-lekarna.com
info@moja-lekarna.com

