Tooth decay (dental caries) is the decay of part of the tooth and is the result of the gradual dissolution of the hard dental substance (enamel) and the progression of this process in depth. Along with colds and gum disease, tooth decay is the most common ailment of humanity. If we don't care for it, the defect gets more extensive and finally destroys the tooth.
CARIES: General | Symptoms | Causes | Diagnosis and Prevention | Treatment | Pulpitis | Periapical abscess | Questions and Answers | Sources/references
Daily brushing and flossing keep teeth healthy. By removing plaque and limiting the amount of sugar you eat, you reduce the likelihood of tooth decay.
Fluoridated water helps significantly.
Image: When tooth decay reaches the pulp, it causes irreparable damage.
.jpeg)
Dental language:
| Lay terms | Professional terms |
| device | orthodontic appliance |
| gum disease | periodontal diseases |
| gum | gingiva |
| stone | calculus |
| crown | cover |
| improper bite | malocclusion |
| baby teeth | baby teeth |
| prevention | prophylaxis |
| laughing gas | nitric oxide |
| lower jaw | mandible |
| front teeth | incisors and under eyes |
| silver seals | amalgam fillings |
| permanent teeth | permanent teeth |
| bite | occlusion |
| oral palate | palate |
| back teeth | cheekbones and molars |
| rabbit lip | cheilosis |
| watering | seal |
| upper jaw | maxilla |
| tooth decay | caries |
Limiting alcoholic beverages and tobacco also helps to improve the health of the mouth and teeth. Tobacco causes inflammation of the gums regardless of whether it is smoked or chewed. Tobacco and alcohol, especially both together, cause oral cancer.
Symptoms
Toothache is not only caused by tooth decay; it can also be caused by an exposed tooth root, chewing too hard, or a cracked tooth. A blocked sinus (paranasal cavity) can also cause sensitivity of the upper teeth.
Enamel decay usually does not cause pain; it occurs when it reaches the dentin. A person may feel pain only while drinking a cold drink or eating sweet food. This shows that the pulp is still healthy. If we start treatment at this stage, the dentist can save the tooth; the patient usually has no more pain or problems with chewing.
When tooth decay reaches the pulp, it causes irreversible damage. Delayed pain after a long-removed stimulus (for example, cold water) or spontaneous pain that appears on its own is typical.
Video content: Hello Dentist 3: Jure Robič Dr. Dent. During.

When the bacteria reach the pulp, it dies, and the pain stops for a while. After a few hours or days, the tooth becomes sensitive to biting and touching with the tongue or finger; as the inflammation and infection spread through the opening in the top of the root to the surrounding area of the tooth, an abscess forms.
Pus collects around the tooth and forces it out of the alveolus (dental cavity). When biting, the tooth returns to its place, which causes severe pain. Pus accumulates continuously, so swelling of the gums can occur near the affected tooth or spread to the jawbone (phlegmon). Pus may drain into the mouth or the skin near the jawbone.
Causes
All factors must be present for tooth decay: a susceptible tooth, bacteria that produce acid and use it to dissolve the tooth, and food for bacteria. A tooth is susceptible if it contains too few fluoride ions, has many holes on the surface, and has pronounced furrows and fissures, where plaque (accumulation of bacteria on the teeth) accumulates. Many bacteria are present in the mouth, but some cause tooth decay. Streptococcus mutans is the most common.
The development of tooth decay depends on its place of origin. The most easily preventable, slowest-progressing, and mildest form is caries of smooth surfaces. It starts as a white stain on the enamel and is caused by bacterial dissolution of its calcium. It usually appears between the ages of twenty and thirty.
During the teenage period, caries occurs on permanent teeth in pits and fissures of the chewing and buccal tooth surfaces. It progresses quickly. Despite consistent washing, many people cannot satisfactorily clean these places due to their inaccessibility.
Image: Tooth decay is caused by bacteria and other things.
-Copy-1.jpg)
Root rot begins on the tooth root's surface, covered by dental cementum—a bone-like tissue. In middle age, the gums recede, and the tooth root becomes exposed. This type of tooth decay is caused by poor brushing and a diet high in sugar. It belongs to the most challenging group of caries to prevent.
Enamel is the most complex outer layer of the tooth, so caries progress slowly. When it penetrates the next, softer, less resistant layer (dentin), it progresses faster towards the pulp, the central part of the tooth, with nerves and vessels. It takes two to three years for decay to break through the enamel but only one year from the dentin to the pulp, even though the distance is much greater. Decay starts in the dentin, destroying a lot of dentin quickly.
Diagnosis and Prevention
The likelihood of pulp damage is lower if tooth decay is removed before pain occurs. In this way, we can preserve most of the dentition. To detect tooth decay early, the doctor will ask about pain, examine the teeth, probe them with dental instruments (to detect tenderness or tenderness), and possibly order an X-ray. A dental examination is necessary every six months, but X-rays are not required at every examination. The dentist decides on the latter, depending on the state of the teeth.
There are five key ways to prevent rot:
- fluorides,
- good oral hygiene,
- adequate nutrition,
- preventive sealing of susceptible places on the teeth and
- treatment with antibacterial drugs.
Oral hygiene Good oral hygiene, which includes brushing before and after breakfast and before bed and daily flossing to remove plaque, can successfully prevent tooth decay on smooth surfaces.
Video content: What causes caries.

Brushing prevents the formation of caries on tooth surfaces, and flossing also cleans places the brush cannot reach. With a gum booster with a rubber attachment, we can remove food residues from under the gum line, the inside of the lips, cheeks, tongue, and palate.
Skilled people usually brush correctly in about three minutes. The coating is soft during the first 24 hours so that it can be easily removed with a soft-bristled toothbrush and floss. In such a short period, the formation of rot is unlikely, but after 24 hours, the coatings are already starting to calcify and are much more difficult to remove.
Treatment
If we stop the development of tooth decay before it reaches the dentin, the enamel can harden on its own, and the white spots on the tooth disappear. When the decay reaches the dentin, the affected part of the tooth must be removed and replaced with a filling. Early treatment of tooth decay is essential to preserve the tooth and dramatically reduces the possibility of pulp damage.
Nutrition
All carbohydrates can cause tooth decay, but the main culprits are sugars. All simple sugars have the same effect on teeth: regular sugar (sucrose), sugars in honey (fructose and glucose), fruit (fructose), and milk (lactose).
When Streptococcus mutans bacteria are found in the coating, they form acid after 20 minutes of contact with sugar. The amount of sugar consumed is not as significant as when it is in contact with the teeth. Sipping a sugary drink every hour is more harmful than licking a chocolate bar for five minutes, even though the bar has more sugar.
Image: People with a greater tendency to tooth decay should limit sweet foods.
.jpg)
People with greater susceptibility to tooth decay should limit sweet foods. Rinsing your mouth with water after eating partially washes away the sweetness, but brushing is more effective. Drinking beverages sweetened with artificial sweeteners is recommended, bearing in mind that some non-alcoholic sodas (diet colas) contain acid that promotes decay. We must drink unsweetened coffee and tea to prevent rot on the exposed root surfaces.
Fluorides increase the resistance of tooth enamel against acids, which dissolve the tooth substance and thus enable the formation of decay. Fluoride preparations are essential until the age of eleven because, during this time, the teeth are hardening (maturing) and growing. Water fluoridation is the most effective way of providing fluoride. We do not fluoridate water in Slovenia, but in the USA, for example, we do. More than half of the population gets enough fluoride to reduce tooth decay through this route.
Too much fluoride intake can cause mottled and discolored teeth. When drinking water does not contain enough fluoride, a doctor or dentist may prescribe sodium fluoride drops or tablets and fluoride toothpaste. A dentist can apply fluoride directly to the teeth, which makes sense in people (regardless of their age) with a greater tendency to tooth decay.
Root tooth treatment
Substances for sealing fissures: We use them to protect hard-to-reach places, especially the cheekbones and molars. After thoroughly cleaning, the dentist prepares the enamel appropriately and then covers the tooth's furrows with a liquid plastic mass.
Procedure:
- The tooth is numbed (anesthetized).
- A rubber membrane (cofferdam) is placed around the tooth to prevent contact of the tooth with bacteria in the mouth.
- For the back teeth, make an opening through the biting surface, and for the front teeth, make it through the lingual side of the tooth.
- We use special instruments to go through the created opening into the pulp canal and remove the remains of the pulp.
- The channel is cleaned and scraped along its entire length.
- Fill the channel with filling material.
The solidified substance becomes an effective barrier for bacteria and food, inhibiting the formation of acids. Sealants are durable; 90 percent remain in place after one year, and 60 percent even after ten years. Minor corrections and replacements are occasionally required.
Some people have highly aggressive cariogenic bacteria in their mouths. It is possible to transfer bacteria from parent to child, especially from kissing. Bacteria thrive well in a child's mouth. Exercise can cause decay of the first erupted teeth. The tendency to tooth decay is not always the result of poor oral hygiene or improper diet in the family.
Image: Covers are usually made of gold alloys or other materials.
.jpg)
It is recommended that people with a greater tendency to tooth decay be treated with antibacterial drugs. The dentist must remove all carious sites and seal all holes and furrows on the teeth. Then, he prescribes a strong mouthwash (chlorhexidine) for a few weeks to kill any bacteria in the lining. The goal is to change the bacterial species in the mouth (preferably less aggressive than cariogenic). Daily fluoride mouthwashes and chewing gum with xylitol are recommended to maintain the condition achieved.
Fillers
Fillings are made of various materials that can be inserted into or around the tooth. We often use silver amalgam for the back teeth because it is very resistant, and color is unimportant in this area. Amalgam is also relatively cheap and lasts up to 14 years. Gold fillings (inlays) are more robust and suitable for severe dental injuries but are more expensive. They require at least two visits to the dentist for their insertion.
Composite resins and porcelain fillings are used for front teeth where the color of amalgam is not suitable. They match the tooth's color and are increasingly used for back teeth.
The tooth-colored vitreous cement (vitreous ionomer) releases fluoride ions, which benefits anyone prone to dental caries. It is used to repair carious lesions near the gums or tooth damage due to excessive brushing. It is very similar in color to a tooth.
Treatment of root canals and tooth extraction
If tooth decay progresses to the extent that it ultimately damages the pulp, the only option to eliminate the pain is to remove the pulp tissue from the root canal or the entire tooth. RootDentally treated back teeth have the best chance of being preserved if their entire chewing surface is coated. For front teeth, the replacement method depends on the amount of intact teeth.
A week or two after root canal treatment, fever, headache, and swelling of the jaw and floor of the mouth or neck may sometimes occur. In such cases, it is necessary to visit a doctor or dentist immediately.
Video content: How to overcome fear of the dentist.

After extraction (pulling out), the tooth must be replaced immediately. If we do not do this, the position of the adjacent teeth changes, which causes chewing disorders. The replacement can be a bridge, i.e., a fixed partial denture in which the adjacent teeth next to the missing tooth are covered with a coating. A removable prosthesis can also be a solution. Replacement of a missing tooth is also possible with an implant.
A crown is a substitute that fits over the tooth. Achieving a good fit requires at least two, and usually more, visits to the dentist. First, the tooth becomes thinner, or the dentist takes an impression and places a temporary covering. The final covering is made in the prosthetics laboratory based on the impression, which is also aesthetically designed. At the next visit, the dentist removes the temporary coating and cements the final coating on the tooth.
Coatings are usually made of gold alloys or other materials. We use porcelain to cover metallic paint; the coating can be entirely porcelain. Because porcelain is harsh and abrasive, it can wear down opposing teeth. Additionally, veneers made only of porcelain or similar materials are more likely to crack than metal veneers.
Pulpitis
Pulpitis is a painful inflammation of the dental pulp, the innermost part of the tooth, with blood vessels and nerves. The most common cause of pulpitis is tooth decay, followed by injuries. The pulp is surrounded by the tooth's rigid walls, which do not allow it to swell when inflamed.
Therefore, the pressure on the vessels and nerves increases in the dental pulp. Mild inflammation is successfully stopped and does not permanently affect the tooth, while severe inflammation destroys the pulp. The increased pressure can push the pulp tissue through the root apex, damaging the surrounding jaw bones and tissues.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The dentist uses various tests to determine the condition of the pulp. If he tests with a cold stimulus and the pain stops a few seconds after removing the stimulus, the pulp is still healthy. The doctor only has to remove the carious part of the tooth and replace it with a filling. If the pain persists after removing the cold stimulus or if it appears spontaneously, the pulp is already so damaged that it cannot be saved.
Picture: Pulpitis causes severe toothache.
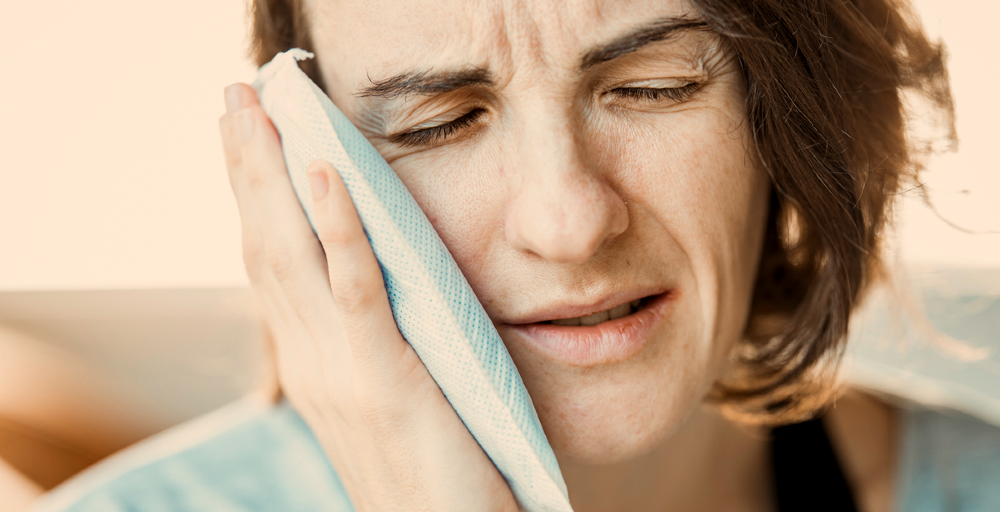

The dentist can also use an electric pulp tester for testing. With it, he gets information about whether the pulp is alive but nothing about the degree of deterioration. The pulp is alive if the affected person feels a slight electrical irritation in the examined tooth.
Tenderness to the touch indicates the inflammation has already spread to the surrounding bone and tissue. The X-ray image confirms the carious decay of the tooth and shows the spread of inflammation with damage to the periodontal bone around the root.
Treatment
Inflammation stops as soon as its cause is removed. Even a temporary filling with a soothing agent can relieve pain in early pulpitis. It should remain for 6 to 8 weeks, after which a final filling must be made, which can sometimes be done immediately. When the pulp is severely and irreparably damaged, the only option to eliminate the pain is to remove it through root canal treatment or tooth extraction.
Periapical abscess
A periapical abscess is an abscess, the cause of which is usually the spread of infection from the tooth to the surrounding tissue. The body is protected from infection by white blood cells, which, in addition to dead tissue, are the main component of pus. Typically, the pus that forms in the tooth due to the infection drains into the gum next to the affected tooth, which swells next to the root of the tooth. Depending on the tooth's position, pus can also ooze through the skin into the mouth, throat, or other areas of the head.
Treatment
The dentist treats an abscess or phlegmon by removing the cause of the infection and draining the pus. He does this through surgery or root canal treatment. He may prescribe antibiotics to ease the infection, but they are more critical for removing diseased pulp and drainage of pus.
Questions and answers
What causes tooth decay in children?
Bacteria and other things cause tooth decay. This can happen when foods containing carbohydrates (sugars and starches) remain on the teeth. Such foods include milk, sweetened beverages, dried fruit, sweets, fruit juices, cereals, and bread. Bacteria that usually live in the mouth change this food and form acids[1].
Can caries be treated only with a filling?
Dental fillings (fillings) are used to treat cavities because the dentist usually wants to remove the decayed part (cavity) and fill it to prevent further damage. While there are no ways to remove a cavity without using a filling, there are ways to nearly reverse the decay[2].
What are the complications of untreated tooth decay?
Untreated tooth decay can cause an abscess (severe infection) under the gums, which can spread to other parts of the body and have serious and, in rare cases, fatal consequences[3].
How to prevent caries?
You can prevent tooth decay by eating a healthy diet, avoiding sugary drinks, drinking plenty of tap water, brushing your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, and flossing daily [4].
Can tooth decay be genetic?
Your genes can affect the development of your teeth, which means that the development of your teeth may be the reason why you are susceptible to problems. While genetics is sometimes the cause of tooth decay, tooth decay can also develop due to poor oral hygiene, smoking, lack of saliva, or flossing[5].
Sources and references
Extensive health manual for home use, Youth Book Publishing House
- Tooth Decay (Caries or Cavities) in Children - https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org
- Is a Dental Filling Always Required for Cavities? - https://www.davidbakerdds.com
- Cavities - https://www.cdc.gov
- Tooth decay - https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au
- Are Cavities Genetic? Here's Everything to Know - https://www.thesuperdentists.com









 Facebook
Facebook
 Instagram
Instagram
 info@moja-lekarna.com
info@moja-lekarna.com

