Vitamin A (retinol, retinoic acid) is a macro-nutrient essential for vision; it also participates in iron metabolism, cell division, immunity, and many other body functions.
Vitamin A: General | Vitamin A for eyes | Vitamin A for the immune system | Vitamin A for skin | Recommended daily intake | Foods with vitamin A | Food supplements | Risks | Shortage | Deficiency Treatment | Questions and Answers | Sources/references
The human body does not produce vitamin A naturally, but it can be found in many foods and is also available as a dietary supplement. If you do not have a diagnosed vitamin A deficiency, it is always best to meet your needs for a specific vitamin through a balanced and healthy diet.
Vitamin A is found in many foods, such as spinach, dairy products, and liver. Other sources are foods rich in beta-carotene, such as green leafy vegetables, carrots, and cantaloupe. The human body converts beta-carotene into vitamin A.
As an oral supplement, vitamin A is particularly beneficial for people with a poor or restricted diet or a medical condition that increases the need for vitamin A. However, if you take vitamin A for its antioxidant properties, the supplement may not provide the same benefits as naturally occurring antioxidants in food.
Image: vitamin A can also be obtained by consuming food supplements.
The two primary forms of vitamin A in the human diet are precursor forms of vitamin A (retinol, retinyl esters) and provitamin A carotenoids, such as alpha-carotene and beta-carotene, which are converted to retinol.
Video content: why is vitamin A also called retinol?

The precursor form of vitamin A comes from animal products, fortified foods, and vitamin supplements. Carotenoids are found naturally in plant foods. Other types of carotenoids are found in food that is not converted to vitamin A but still promote health and is incorporated into many nutritional supplements; these include lycopene, lutein, and zeaxanthin.
Benefits of vitamin A for the eyes
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining vision, forming pigments that help the eye see color. Without vitamin A, your eyes stop producing these important eye pigments, which can eventually lead to night blindness - this causes difficulty adjusting to low light or a complete inability to see in the dark.
Vitamin A also plays a vital role in protecting the eye's cornea, the transparent outer layer. This can reduce the risk of developing cataracts, which cause blurred vision. Cataract is a common eye disease that affects more than half of people over the age of 80.
Image: vitamin A forms pigments that help the eye see color.
Vitamin A in adequate amounts can also prevent blindness in childhood, as it plays a crucial role in early eye development. Therefore, it is always recommended to follow this vital vitamin intake, as vitamin A deficiency leads to poor vision.
Benefits of vitamin A for the immune system
Vitamin A takes care of the immune system and maintains and strengthens the epithelium and mucous tissues surrounding most of our organs. These tissues are the body's first line of defense against pathogens and are vital to the body's innate immune response to infection.
Susceptibility to infections is known to increase, especially in developing countries, due to a lack of vitamin A. Vitamin A is closely related to retinoids and carotenoids, but both work in the body through the most active form, trans-retinoic acid. In addition to the response of immune cells, vitamin A also plays a vital role in mucus secretion, morphological formation, and functional maturation of epithelial cells.
By adding vitamin A, it contributes to the development of immunity by regulating the response of immune cells and ensuring mechanical defenses. Vitamin A has received particular attention in recent years, as it has been shown to have a crucial effect on the immune response.
Benefits of vitamin A for skin
A type of vitamin A available by prescription or in smaller doses in over-the-counter products called retinol is considered one of the best topical acne treatments. Acne care and treatment guidelines suggest using topical retinoids or products with retinol as the first line of treatment for mild to severe acne.
Video content: skin care while using Isotretinoin (Roaccutane).

Isotretinoin (Roaccutane) is a vitamin A derivative known as a retinoid. Your body reacts to it similarly to vitamin A. Accutane helps treat acne by shrinking oil glands (sebaceous glands), preventing clogged pores, reducing the growth of skin bacteria, and having anti-inflammatory effects.
Among other things, vitamin A and beta-carotene reduce anemia, as they maintain good permeability of iron in the intestinal lumen and prevent the inhibitory effect of phytates and polyphenols on iron absorption. Therefore, the simultaneous use of iron and vitamin A supplements is a more effective method for preventing iron deficiency anemia than using these micronutrients alone.
How much vitamin A should be consumed?
The recommended intake of vitamin A varies according to age and period of life (e.g., pregnancy, breastfeeding). However, consuming 770 mcg of this vital vitamin during pregnancy and breastfeeding is necessary, as much as 1,300 mcg per day.
The recommended daily intake of vitamin A according to age, gender, and period of life is as follows:
| Age/life span | Recommended daily intake |
| From birth to 6 months | 400 mcg |
| From 7-12 months | 500 mcg |
| From 1-3 years | 300 mcg |
| From 4-8 years | 400 mcg |
| From 9-13 years | 600 mcg |
| From 14-18 | 900 mcg |
| From 14-18 | 700 mcg |
| Grown men | 900 mcg |
| Grown women | 700 mcg |
| Pregnant teenage girls | 750 mcg |
| Adult pregnant women | 770 mcg |
| Nursing teenage girls | 1200 mcg |
| Nursing adult women | 1,300 mcg |
Image: if you are pregnant, your baby needs vitamin A for healthy growth and development.

For adults, the upper limit of vitamin A is 3000 mcg. Vitamin A during pregnancy should not exceed 3000 mcg per day. Since vitamin A is fat soluble, the body will store excess amounts. Taking too much vitamin A is not recommended - it can increase concentrations of this otherwise essential vitamin to toxic levels, affecting your liver's function, a condition known as hypervitaminosis A.
Foods with vitamin A
Animal and plant food sources provide different types of vitamin A. The readily assimilated type by the body is known as preformed vitamin A or retinol.
Excellent sources of retinol include:
- eggs
- oily fish
- cheese
- milk
- yogurt
- liver
The liver is a good source of vitamin A but should be consumed cautiously. Pregnant women should avoid eating liver and liver products such as pate. Vitamin A also exists in abundance in the form of beta-carotene.
Image: vitamin A is best consumed from the daily diet.
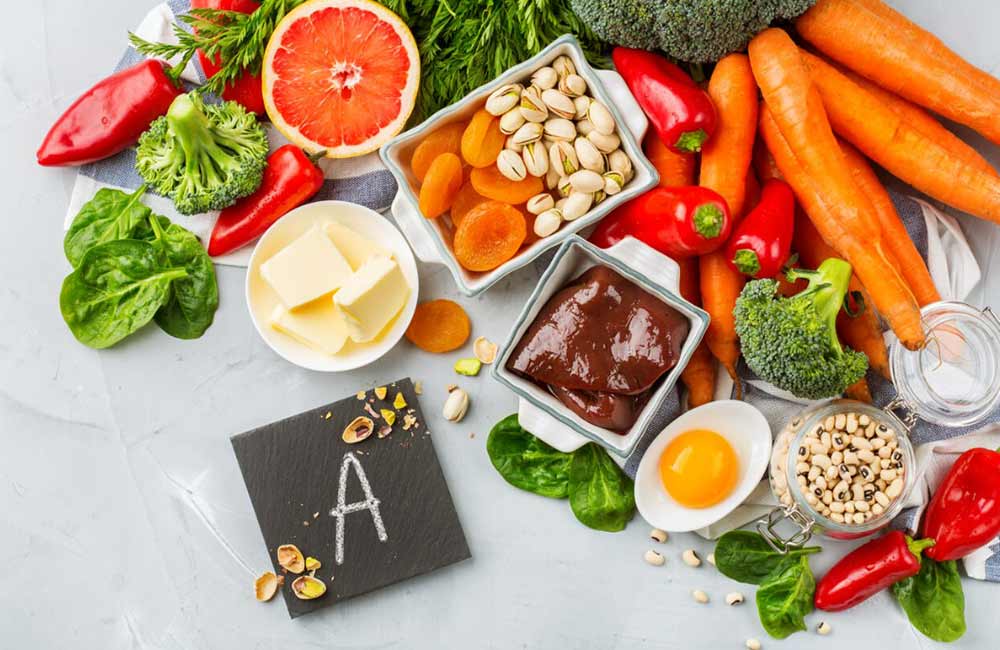

The primary sources of beta-carotene include:
- green leafy vegetables
- red, orange, and yellow vegetables
- sweet potato
- yellow fruit
Food supplements with vitamin A
Vitamin A supplements can cover the deficiency if food sources do not contain sufficient amounts of this micronutrient. Your vitamin supplement A may contain preformed vitamin A, provitamin A, or a combination. Knowing how much vitamin A precursors you are taking is especially important in preventing toxicity, as synthetic vitamin A can cause your body to reach dangerous vitamin A levels.
Look for a vitamin A supplement that contains some fat in the form of an oil to help your body absorb vitamin A and other fat-soluble vitamins. Vitamin A comes from two sources - preformed vitamin A, which comes from animal sources and includes retinol, and anti-vitamin A, or carotenoid, which comes from plants and includes beta-carotene.
Video Content: 7 Signs You Need More Vitamin A.

Examples of good vitamin A supplements include:
- fish liver oil
- multivitamins
- retinoid supplements
Risks of taking vitamin A supplements
Excessive consumption of vitamin A can cause adverse side effects, which can be life-threatening. Therefore, it is by no means recommended that you consume more than 3,000 micrograms of vitamin A per day from any or all sources except under the supervision of a physician. This restriction does not apply to vitamin A, whose origin is carotenoids. Provitamin A does not pose the same risks as preformed vitamin A.
Hypervitaminosis A – or vitamin A toxicity – can occur after taking a single large dose of vitamin A or smaller doses over a long period.
Symptoms include:
- headache
- release
- sleepiness
- abdominal pains
- nausea
- vomiting
- skin peeling
- dry eyes
Figure: Do not take more than 3,000 micrograms of vitamin A daily unless under medical supervision.

If you overeat carotene, you can develop carotenemia. Carotenemia can cause your skin to turn yellow but usually causes no other symptoms. Although carotene is converted to vitamin A in the body, excess carotene does not cause vitamin A toxicity.
If you are pregnant, your baby needs vitamin A for healthy growth and development. However, too much-preformed vitamin A can cause congenital disabilities in your baby. Therefore, pregnant women should avoid supplements containing more than 1500 micrograms of RAE.
Vitamin A deficiency
With vitamin A deficiency, your body lacks this essential vitamin needed for proper functioning. Vitamin A deficiency can cause vision loss and blindness, but it can also cause skin, heart, lungs, tissues, and immune system complications. While deficiency is rare in developed countries, many people in developing countries do not get enough vitamin A. Pregnant women, nursing mothers, infants, and children are also at the most significant risk of deficiency.
Image: vitamin A plays a vital role in protecting the cornea, the eye's transparent outer layer.

One of the early signs of vitamin A deficiency is night blindness (nyctalopia). When vitamin A deficiency worsens, the sclera and cornea can dry, and the eye cannot produce tears (xerophthalmia). In addition, Bitot's spots may appear on the whites of your eyes. There may even be open wounds on the cornea or drying or clouding of the cornea (keratomalacia), which can lead to blindness.
Vitamin A deficiency can cause many complications, including the following:
- eye problems
- skin problems
- infertility
- growth problems
- respiratory tract infections
Vitamin A deficiency can also be caused by diseases and conditions that reduce your gut's ability to absorb fat. These conditions can reduce your body's ability to absorb vitamins such as vitamin A.
These states include:
- chronic diarrhea
- cystic fibrosis
- blockade of the bile ducts
- zinc or iron deficiency
- certain diseases of the pancreas
- intestinal or pancreatic surgery
- small bowel bypass or bariatric surgery
- alcohol use disorder
Vitamin A deficiency diagnosis and treatment
A doctor can diagnose vitamin A deficiency based on your symptoms and a blood test. For example, if you have night blindness, your doctor may order an eye test called electroretinography. Electroretinography examines the light-sensing cells (photoreceptors) in your retina. The test measures your retina's response to flashes of light.
Image: A doctor will treat vitamin A deficiency with high-dose vitamin A supplementation.

A blood test can measure the amount of vitamin A in your blood. However, your body stores large amounts of vitamin A, so your blood levels of vitamin A will not drop until your deficiency is severe. A vitamin A deficiency can be confirmed if your symptoms improve after taking a vitamin A supplement.
Your doctor will treat vitamin A deficiency with high-dose vitamin A supplements. After a few days, you will be given lower doses of vitamin A until the problems with low levels improve. Vitamin A supplements can cure night blindness and help re-moisturize the eyes. However, the loss of vision due to scarring due to corneal ulcers is unfortunately not curable.
Your doctor can help you plan a healthy, balanced diet that includes primarily foods that contain vitamin A. If you have a retinol level above 30 mcg/dL, vitamin A supplementation will not help. The best way to prevent vitamin A deficiency is a healthy diet.
Questions and answers
Do we need more vitamin A during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, the need for vitamin A increases by approximately 10% to 20%, but in any case, do not overdo it using such supplements; stick to the recommended values.
- Pregnant teenagers: 750 mcg
- Adult pregnant women: 770 mcg[1]
Which foods contain the most vitamin A?
Animal and plant food sources provide different types of vitamin A. The type of vitamin A readily assimilated by the body is known as preformed vitamin A or retinol. Vitamin A also exists in abundance in the form of beta-carotene. Vitamin A and beta-carotene can be found in foods such as eggs, fatty fish, cheese, milk, yogurt, liver, green leafy vegetables, red, orange, and yellow vegetables, sweet potatoes, and yellow fruits[2].
Image: Acne treatment and care guidelines suggest using topical retinoids or products with retinol.

What are the benefits of vitamin A in skin care cosmetics?
Vitamin A helps speed up skin regeneration, prevents breakouts and supports the skin's immune system, and promotes natural hydration - that means it effectively hydrates the skin and gives it a radiant glow, helps promote and maintain a healthy dermis and epidermis - the top two layers of your skin[3].
Sources and references
1. Vitamin A and Carotenoids - https://ods.od.nih.gov2. Vitamin A - https://www.hsph.harvard.edu
3. The Benefits — and Limits — of Vitamin A for Your Skin - https://www.healthline.com











 Facebook
Facebook
 Instagram
Instagram
 info@moja-lekarna.com
info@moja-lekarna.com

