Astma je bolezen, ki prizadene predvsem vaša pljuča. Je ena najpogostejših dolgotrajnih bolezni otrok in odraslih. Astma povzroča piskajoče dihanje, težko dihanje, tiščanje v prsih in kašelj ponoči ali zgodaj zjutraj. V nadaljevanju pa predstavljamo tudi številne težave povezane z dihali in dihalnimi težavami.
ASTMA: Simptomi astme | Posvet z zdravnikom | Vzroki astme | Diagnostični postopki | Zdravljenje | Konvencionalna medicina | Alternativni načini | Preprečevanje | Miti in dejstva | Vprašanja in odgovori | Viri/reference
DIHALA, TEŽAVE, TEŽKO DIHANJE: Simptomi | Posvet z zdravnikom | Vzroki dihalnih težav | Diagnostični postopki | Zdravljenje | Konvencionalna medicina | Alternativni načini | Zdravljenje doma | Vprašanja in odgovori | Viri/reference
PLJUČNICA: več na voljo na povezavi Pljučnica
PLJUČNI RAK: več na voljo na povezavi Pljučni rak
PLEVRITIS: več na voljo na povezavi Plevritis
Astma je kronična težava z dihanjem, ki lahko vpliva na vsakogar, ne glede na starost. V osnovi gre za vnetje dihalnih poti, kar povzroča težave z dihanjem, kašelj in piskanje. Morda ste že slišali za to stanje, ampak kako resno je v resnici?
No, astma je pogostejša, kot si morda mislite, in prizadene milijone ljudi po vsem svetu. Simptomi se lahko razlikujejo – nekateri ljudje občutijo le občasno nelagodje, medtem ko drugi doživijo hude napade, ki zahtevajo nujno pomoč.
Simptomi
- Nemir ali nespečnost.
- Vedno večji, vendar razmeroma neboleč pritisk v prsih.
- Blago do zmerno izražena kratka sapa.
- Piskajoč ali žvižgajoč zvok ob dihanju, ki je po jakosti lahko povsem tih ali zelo glasen.
- Kašelj, ki ga včasih spremlja gnojni izpljunek.
POSVETUJTE SE Z ZDRAVNIKOM, ČE:
- vi ali kdo drug prvič doživite astmatični napad; astma je kronična bolezen, ki je lahko zelo resno stanje, če je ne zdravimo pravilno.
- predpisano zdravilo zoper astmo po določenem času, ko bi že moralo delovati, ne deluje; potrebujete drugo zdravilo ali pa imate zelo hud napad,
- vi ali kdo drug, ki ima astmo, začutite dušenje, zaradi katerega težko govorite;
- plapolajo nosnice, če se koža med rebri vidno vgreza in kadar so ustnice ali koža pod nohti videti sive ali modrikaste barve. To so znaki hudega pomanjkanja kisika. Poiščite nujno pomoč in takojšnje zdravljenje.
Astma je kronična bolezen dihal, ki podobno kot bronhitis ali emfizem povzroča občutek stiskanja v prsih in težave z dihanjem.
Slika: Prerez prikaza stanja ob astmatičnem napadu.
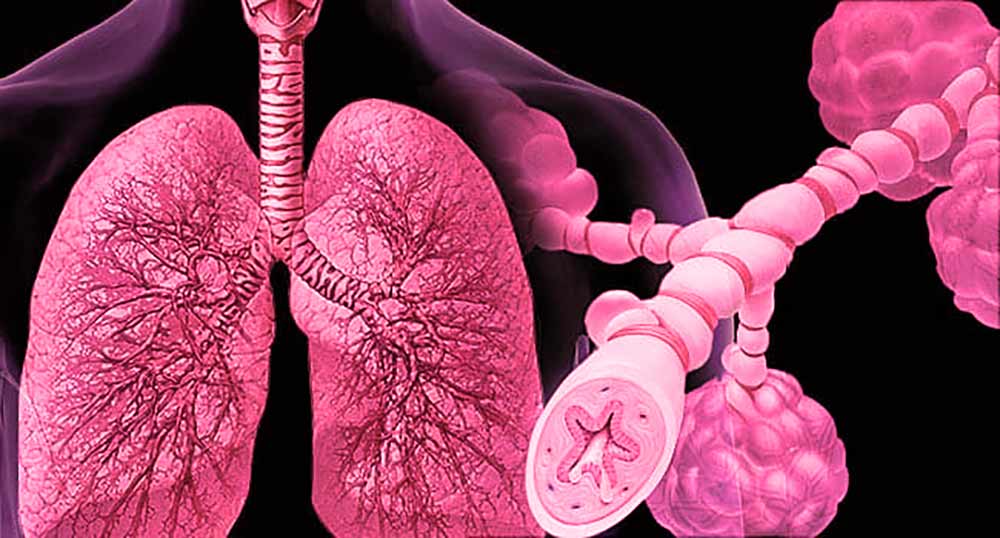
Vendar pri astmi ti simptomi niso vedno prisotni. Pojavljajo se v napadih, ki jih lahko sprožijo različni »sprožilci« iz okolja ali so čustveno pogojeni, npr. pelodi, živalska dlaka, cigaretni dim in stres.
Nekateri ljudje z astmo imajo le blage in redke napade, zato jih to stanje moti le občasno. Pri drugih pa so lahko napadi pogosti in hudi ter terjajo urgentno zdravljenje. Če imate astmo, morate redno hoditi na zdravniške preglede in pri hujšem napadu takoj poiskati nujno pomoč in zdravljenje. Če poznate sprožilne dejavnike, se boste lahko naučili zmanjšati število napadov in njihovo jakost, morda pa se jim boste celo znali povsem izogniti.
Astma ni težava, pri kateri ne bi mogli vdihniti, ampak težava, pri kateri ne morete izdihniti. Med astmatičnim napadom mišični krči in otekanje tkiva bronhov zožijo tanke dihalne poti v pljučih, ki se nato še zamašijo s preobilno nastajajočo sluzjo.
Nesvež zrak je ujet na dnu pljuč. To vas prisili, da uporabljate zgornje dele za hlastanje za zrakom. Blagi in zmerni napadi potekajo kot kratke epizode, med katerimi lovite sapo in piskate. V hudih primerih pa se dihalne poti v pljučih tako zožijo in zamašijo, da onemogočijo dihanje.
Video vsebina: Astma - animacija.

Tak napad lahko mine hitro ali pa traja ves dan. Včasih se simptomi nenadoma ponovijo, in sicer z neverjetno jakostjo. Tak »drugi val« napada je lahko hujši in bolj nevaren kot prvi napad in lahko traja dneve ali celo tedne.
Astma je dokaj pogosta bolezen. Pri otrocih je pogostejša kot pri odraslih in je pogost vzrok izostajanja od pouka in sprejemov na otroške oddelke bolnišnic. Čeprav je le redko smrtna, je lahko prav resna bolezen. Če imate astmo, morate po pomoč k zdravniku, preden se odločite za morebitne alternativne načine zdravljenja.
Vzroki
Astma ni posledica le enega vzroka, ampak sprožijo napad zelo različni in številni dejavniki, ki delujejo sami ali v kombinaciji. Med vodilnimi vzroki so alergije. Približno 50 do 90 % ljudi z astmo je alergičnih.
Najpogostejši alergeni ali substance, ki sprožajo alergije, so pelodi, trave, prah, plesni, tobačni dim in živalska dlaka. Če jih vdihnemo, lahko take snovi sprožijo sproščanje histamina in drugih kemičnih snov v telesu. Te povzročajo alergijsko reakcijo in napade astme.
Med druge alergene uvrščamo še kemične hlape; acetilsalicilno kislino ali njej podobne snovi, npr. fenilbutazon, indometacin, ibuprofen in druga nesteroidna protivnetna zdravila; ter sulfite, ki jih v visokih vsebnostih najdemo v določenih vrstah hrane ali pijači.
Med dejavniki za nastajanje astme, ki je povezana z alergijo, je tudi dednost: znanstveniki so odkrili gen, zaradi katerega, kot kaže, so nekateri ljudje bolj dovzetni za to bolezen. Astmo lahko sprožijo tudi okužbe. Bronhiolitis, virusna okužba dihal, ki jo ponavadi dobe otroci, mlajši od dveh let, je zelo pogost vzrok otroške astme. Pri odraslih se lahko astma razvije kot posledica okužbe zgornjih dihal, npr. bronhitisa.
Med druge sprožilce astme prištevamo še telesne dejavnosti, čustveni stres in strese iz okolja npr. onesnaženost zraka.
Astmatična dihala
V zamašena dihala se ujame zrak in dihanje postane oteženo.
Slika: Prikaz normalnih zdravih pljuč in pljuč v trenutku astmatičnega napada.
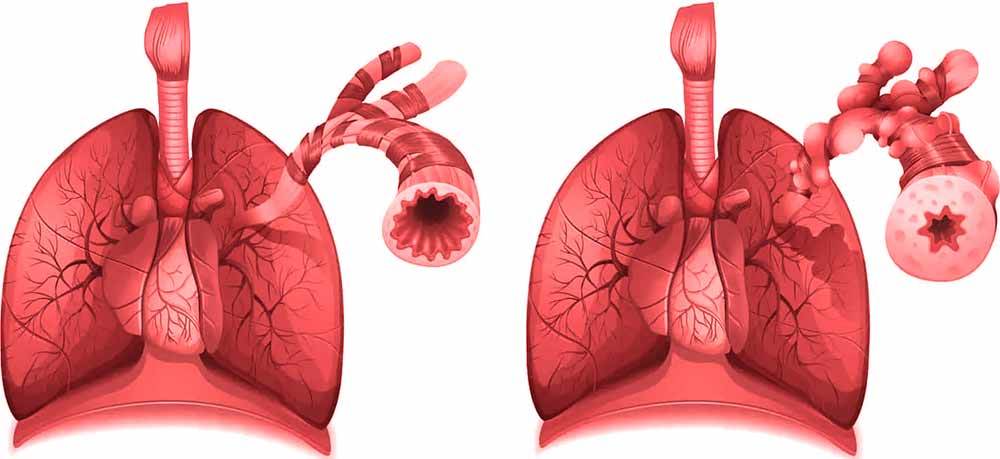
Zrak potuje navzdol po sapniku in vstopa v pljuča skozi cevke, ki jih imenujemo sapnice. Sapnice se delijo. V normalnih pogojih jih obdaja tanka sluznica. Pri ljudeh z astmo lahko določeni pogoji ali vdihavanje določenih snovi delujejo kot »sprožilci«, kar povzroča sproščanje kemičnih snovi, ki zožijo sapnice in proizvajajo obilo sluzi.
DIAGNOSTIČNI POSTOPKI
Za potrditev astme bo zdravnik naročil preiskavo pljučnih funkcij, s katero merijo moč izdiha. V normalnih pogojih lahko človek, ki nima astme, izdihne okoli 75 do 85 % zraka v pljučih v eni sekundi in jih povsem izprazni v treh sekundah.
Oseba z astmo pa potrebuje šest ali sedem sekund, da iztisne zrak iz pljuč. Najpogostejši test pljučnih funkcij je merjenje največjega pretoka. Opravi se z napravo, s katere je mogoče odčitati največji pretok zraka med izdihom. Zdravnik vam lahko napravo predpiše na poseben recept. Tako boste lahko merilnik imeli doma, da boste svoje stanje ves čas nadzirali.
ZDRAVLJENJE
Če imate astmo, morate redno hoditi k zdravniku.
Video vsebina: zdravljenje astme

Pri hudih stanjih je vedno potrebno konvencionalno zdravljenje. Seveda pa obstaja vrsta alternativnih zdravil, ki so lahko zelo uspešna, če jih jemljete kot dodatek konvencionalnemu zdravljenju.
KONVENCIONALNA MEDICINA
Po potrjeni diagnozi, da imate astmo, je prvi korak, da skupaj z zdravnikom izdelate načrt zdravljenja. Kot sestavni del načrta vam bo zdravnik verjetno predlagal, da si dnevno beležite v dnevnik, kateri so morebitni dejavniki iz okolja ali čustveni dejavniki, ki pri vas sprožijo astmatični napad. To ne bo pomagalo le zdravniku, da bo laže nadziral vašo bolezen, temveč tudi vam, da boste spoznali sprožilce astmatičnih napadov in se jim lahko izognili.
Zdravniki za zdravljenje astme z zdravili ponavadi predpišejo bronhodilatatorje, zdravila, ki pomagajo razširiti zožene dihalne poti v pljučih. Ta zdravila je mogoče uporabljati v dveh oblikah, in sicer kot pršila ali kot tablete. Bronhodilatatorji v obliki pršil (včasih celo z dodatkom za odmerjanje količine) so podobni adrenalinu. Zdravniki ponavadi priporočajo bronhodilatatorje v obliki pršil, npr. izoproterenol, metaproterenol, izoetarin in albuterol, ker ti pridejo neposredno v pljuča in je v njih kar 1000-krat manj zdravila kot v tabletah.
Ponavadi en ali dva vpiha zadostujeta za omilitev piskanja in občutka stiskanja v prsih pri blagih in zmernih oblikah napadov.Bronhodilatatorji so močna zdravila. Če jih uporabite v prevelikih odmerkih, se lahko pojavijo nevarni stranski učinki, na primer visok krvni tlak.
Video vsebina: Astma in zdravljenje COPD.

Med bronhodilatatorje, ki jih zaužijemo, sodijo teofilin, metaproterenol, albuterol in terbutalin, in sicer so lahko v obliki sirupa, tablet ali kapsul. Pogosto jih predpišejo ljudem, ki ne prenašajo pršil, ali tistim, ki trpijo zaradi kronične astme. V hudih primerih vam bodo morda predpisali kortikosteroide, vendar mora zdravnik tovrstno zdravljenje skrbno nadzirati, ker se lahko pojavijo nevarni stranski učinki.
V nujnih stanjih boste morda potrebovali injekcijo ali vpihe adrenalina za odprtje dihalnih poti v pljučih. Če vam astmo sprožajo alergije (zlasti na pelode ali pike žuželk), bo zdravnik morda priporočal imunoterapijo. S postopnim izpostavljanjem telesa določenim alergenom (s serijami injekcij) bo vaš imunski sistem postopno zgradil obrambo. Sčasoma se bodo alergijske reakcije omilile ali pa celo povsem izginile.
ALTERNATIVNI NAČINI
Mnogi ljudje poročajo o dobrih uspehih alternativnega zdravljenja, vendar tudi zagovorniki tovrstnega zdravljenja priporočajo to le kot dodatek h konvencionalnim načinom.
Pomnite: Ko vam postavijo diagnozo astme, mora bolezen nadzirati zdravnik. V hudih primerih boste vedno potrebovali konvencionalno zdravljenje.
AKUPRESURA
Nelagodje pri astmi lahko omili nežen pritisk na določene točke telesa. Z desnico pojdite preko leve rame in močno pritisnite na hrbtu med levo lopatico in hrbtenico (točka Mehur 13), petkrat globoko vdihnite; nato to ponovite še na drugi strani. Lahko pa na prsni koš položite pesti, s palcem navzgor, in poiščete občutljivo točko, blizu prsnice tik pod ključnico (točka Ledvice 27). Nanjo dve minuti močno pritiskajte.
AKUPUNKTURA
Več zdravstvenih študij je potrdilo, da lahko akupunktura olajša simptome pri astmi. Postopek lahko izvaja le akupunkturist z licenco.
AROMATERAPIJA
Eterična olja, kot so evkaliptus (Eucalyptus globulus), ožep (Hyssopus officinalis), janež (Pimpinella anisum), sivka (Lavandula officinalis), bor (Pinus sylvestris) in rožmarin (Rosmarinus officinalis), lahko olajšajo dihanje in zmanjšajo zamašenost nosu.
Slika: aromatična eterična olja kot smaopomoč pri astmatičnih zapletih

Vdihavamo jih skozi nos, tako da kapnemo nekaj kapljic na robček ali drug kos tkanine, in s tem olajšamo dihanje pri blagem napadu astme. Če imate tudi sicer občutek zamašenega nosu (ne samo med napadom), zmešajte nekaj kapljic eteričnih olj v posodi, polni vroče vode, čez glavo si dajte brisačo in vdihavajte dišečo paro skozi nos.
KITAJSKA ZELIŠČA
Kitajsko zelišče efedra (Ephedra sinica) je zelo močno bronhodilatatorsko sredstvo.
OPOZORILO: Velike količine tega zelišča imajo lahko enak učinek kot velike količine adrenalina; efedre ne smete uporabljati, če imate visok krvni tlak ali srčno bolezen. Pripravite poparek kombinacije 5 gramov kafre, 4 gramov cimetnih palčk (Cinnamomum cassia), 1,5 grama uralskega sladkega korena (Glycyrrhiza uralensis) in 5 gramov mareličnih pešk (Prunus armeniaca). Mešanico namakajte v hladni vodi, nato pa zavrite in pijte vročo.
ZELIŠČA
Veliki oman (Inula helenium) je korenika, ki deluje kot blago sredstvo za izkašljevanje, zato lahko iz telesa očisti čezmerno sluz.
Video vsebina: 5 naravnih načinov za lajšanje astme in preventivo.

Zvarek pripravite iz 1 kavne žličke zdrobljene korenine. Prelijte jo s polno skodelico hladne vode; stoji naj 10 ur, nato precedite in pijte vroče trikrat dnevno. Poparek, ki ga naredite iz drobnocvetnega lučnika (Verbascum thapsus), priporočajo za ublažitev sluznice dihal, zlasti ponoči.
HOMEOPATIJA
Homeopati priporočajo vrsto zdravil za ublažitev astmatičnih simptomov. Našteli homo le nekatere: za umiritev nemira in tesnobe vzemite arsenicum album (30 C), kolikorkrat je potrebno.
Za simptome, ki se poslabšajo ponoči ali v hladnem vremenu ali pa se pojavijo iznenada vzemite akonit (C6), kolikorkrat je potrebno. Za simptome, ki se poslabšajo na vlažnem, vzemite natrium sulphuricum, kolikorkrat je potrebno. O drugih zdravilih pa se posvetujte s homeopatom, ki ima licenco.
REFLEKSOLOGIJA
Masirajte kožo med palcem in kazalcem na nogi; ta predel naj bi ustrezal grlu in pljučem. Nato raztegnite prste na nogi in masirajte blazinico na stopalu; to področje naj bi odgovarjalo pljučem in prsnemu košu.
JOGA
Joga lahko pomaga, da globlje dihate in se sprostite, s čimer pripomorete k bolj učinkovitemu kljubovanju stresu, ki je pogost sprožilcu astme.
PREPREČEVANJE
- Naučite se prepoznavati sprožilce: v dnevnik si nekaj mesecev vsak dan vpisujte vse dejavnike iz okolja ali prehranske dejavnike, ki vplivajo na vas. Kadar imate napad astme, poglejte v svoj dnevnik in ugotovite, kateri dejavnik ali katera kombinacija dejavnikov bi lahko prispevala k temu.
Slika: povzročitelji astme. Izogibajte se jim v največji možni meri
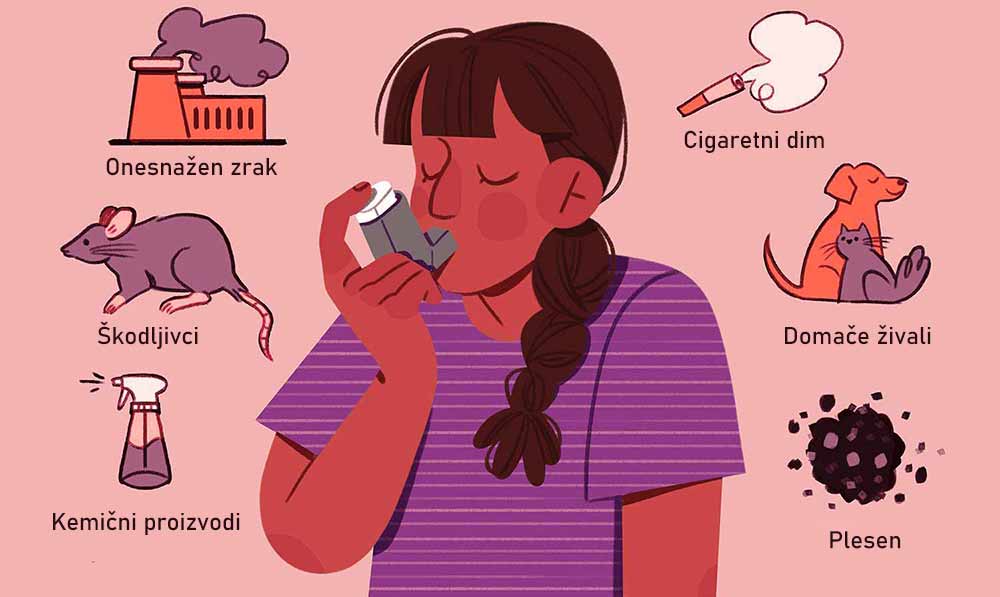
- Zapisujte si spremembe ali nihanja kapacitete pljuč, izmerjene z merilnikom največjega pretoka, ki ga predpiše zdravnik. Če se boste zavedali svoje slabše sposobnosti za izdih, lahko že s preventivnimi ukrepi zmanjšate jakost napada astme.
Video vsebina: kako preprečiti astmatične napade?

- Izogibajte se hrane in napitkov, ki vsebujejo veliko sulfitov, npr. piva, vina, kisa, instantnega čaja, grozdnega soka, limoninega soka, grozdja, svežih rakcev, testa za pico in posušenega sadja (npr. marelic ali jabolk), konzervirane zelenjave, instant krompirjevega pireja, koruznega sirupa, sadnih prelivov in melas. Nekateri dietetiki priporočajo, da se čim bolj izogibate hrani, ki ustvarja veliko sluzi, na primer mleku.
- z dnevnim odmerkom vitaminov B kompleksa (50 do 100 mg) in magnezija (400 do 600 mg) lahko zmanjšate pogostnost in jakost astmatičnih napadov.
ASTMA - MITI IN DEJSTVA
MIT: Ljudje z astmo ne bi smeli telovaditi.
DEJSTVO: Razgibavanje je prav tako pomembno za ljudi z astmo kot za vsakogar drugega. Če so opremljeni z ustreznimi zdravili, lahko ljudje z astmo telovadijo kolikor hočejo.
Pomnite: Mnogi zdravniki ljudem z astmo priporočajo plavanje, ker vlaga olajša dihanje. Seveda pa lahko klor v bazenih povzroči alergijsko reakcijo in sproži napad astme.
MIT: Astmo boste prerasli.
DEJSTVO: To je lahko res, a ne vedno. Čeprav nekako polovica ljudi, ki so astmo imeli med 2. in 10. letom starosti, astmo navidez »preraste«, se bolezen vendarle lahko povrne, ko pridejo v trideseta leta. Prav tako lahko astmo dobite tudi v odrasli dobi, čeprav je kot otrok niste imeli.
MIT: Matere, ki imajo alergijo, ne bi smele dojiti.
DEJSTVO: Dojenčki, ki jih matere dojijo, imajo manj alergij kot dojenčki, ki niso dojeni.
Astma je resna bolezen, zato je potrebno pravočasno prepoznati njene simptome in se na njih tudi pravočasno odzvati.
DIHALA, TEŽAVE, TEŽKO DIHANJE
SIMPTOMI
- Piskanje in dihanje z naporom.
- Kašelj in izkašljevanje sluzi,
- Mrzlica in vročina.
- Utrujenost.
Dihalne težave lahko spremljajo:
- hitro dihanje in hiter utrip;
- kratka sapa;
- bolečine v prsnem košu;
- blag glavobol;
- splošna utrujenost;
- simptomi prehlada: izcedek iz nosu, vneto žrelo in kihanje.
POSVETUJTE SE Z ZDRAVNIKOM, ČE:
- prehlad ali kašelj trajata več kot 7 ali 10 dni in se ne izboljšata z zdravili v prosti prodaji.
- imate občutek napetosti v obrazu, pritisk za očmi, pocejanje v žrelo in slab vonj. To so znaki sinuzitisa.
- kašljate že dalj časa, izkašljujete obarvano sluz ali imate kratko sapo. To so lahko znaki bronhitisa, emfizema ali pljučnega raka.
- imate visoko vročino (nad 38,5 °C), mrzlico, bolečine v prsnem košu in kašelj s krvavkastim izpljunkom. To so lahko znaki pljučnice ali druge resne bolezni.

- tako težko dihate, da ste zaskrbljeni; težko dihanje povzročajo mnoge bolezni.
Dihalne težave razdelimo v tri skupine: okužbe zgornjih in spodnjih dihal, npr. prehlad, sinuzitis, pljučnica in tuberkuloza; kronične obstruktivne pljučne bolezni, npr. astma, bronhitis in emfizem; in poklicne pljučne bolezni, nidr. azbestoza in pnevmokonioza.
VZROKI
Okužbe dihal, ki so ali blage ali zelo nevarne, povzročajo predvsem virusi in bakterije, ki se naselijo v dihalnih poteh. Sposobnost telesa, da premaga te okužbe, je odvisna od starosti, prisotnosti ali odsotnosti drugih bolezni in od kajenja.
Vzroki kroničnih obstruktivnih bolezni so številni. Kronično vnetje pljučnega tkiva, značilno za astmo, lahko npr. sprožijo pelod, dražljive snovi v zraku in telesna vadba. Propadanje pljučnega tkiva, ki je posledica emfizema, nastane zaradi kajenja ali prirojene encimske napake.
Poklicne pljučne bolezni nastanejo zaradi preobčutljivosti posameznika za snovi na delovnem mestu ali zaradi vdihovanja določenih tujih snovi, kot so azbestna vlakna, premogov ali silicijev prah (povzroča silikozo).
DIAGNOSTIČNI POSTOPKI
Zdravniki za opredelitev bolezni dihal uporabljajo številne diagnostične postopke in preiskave, mdr. rentgensko slikanje prsnega koša, druga slikanja pljuč, računalniško tomografijo (CT) , analize vzorcev izpljunka in teste pljučne funkcije.
Kadar potrebujejo specifične podatke, uporabijo invazivne preiskave. S plinsko analizo arterijske krvi (PAAK) npr. določijo koncentracijo kisika in ogljikovega dioksida v krvi; s pljučno biopsijo dobijo vzorce, ki jih pregledajo pod mikroskopom
KJE SE POJAVIJO TEŽAVE?

Zgornja dihala — obnosne votlino, nos. usta in žrelo - so mesto bolezni, kot sta prehlad ali sinuzitis.
Spodnja dihala so mesto hujših in dolgotrajnejših motenj.
Astma in bronhitis prizadeneta sapnik in velike sapnice, pljučnica in emfizem pa okvarita delovanje mikroskopsko majhnih zračnih mešičkov v pljučih.
ZDRAVLJENJE
Okužbe dihal se večinoma same pozdravijo v enem tednu ali 10 dneh. Konvencionalna in alternativna medicina ponujata vrsto preprostih zdravil za zmanjšanje simptomov.
KONVENCIONALNA MEDICINA
Če imate bakterijsko okužbo dihal, vam bo zdravnik predpisal ustrezen antibiotik. Pri prehladu, sinuzitisu in akutnem bronhitisu se boste bolje počutili, če počivate v postelji, pijete veliko tekočine, zvečate vlažnost zraka v prostoru (ali inhalirate paro) in jemljete zdravila proti vročini in bolečinam, če kadite, vam bo zdravnik svetoval, da nehate.
Pri kroničnih obstruktivnih boleznih, kot sta astma in emfizem, pomagajo inhalacijska zdravila. Za poklicni pljučni bolezni azbestozo in silikozo ni učinkovitega zdravljenja, razen da prekinete izpostavljenost snovem, ki dražijo dihala - tudi pasivnemu dimu, in če kadite, da nehate.
ALTERNATIVNI NAČINI
Alternativni načini zdravljenja pomagajo lajšati simptome dihalnih težav. Aromaterapevt ali zeliščar vam lahko svetujeta eterična olja in zelišča za masaže in parne inhalacije, ki zmanjšajo kongestijo in umirijo vnetje. Strokovnjak kitajske medicine lahko priporoča akupunkturo, akupresuro ali številna kitajska zelišča. Homeopati za dihalne težavo predpisujejo širokem palete zdravil. Zdravniki se večinoma strinjajo, da z zdravo prehrano in pravilnimi prehranjevalnimi navadami imunski sistem okrepite in ohranite zdravega. Poskusite priporočene dnevne odmerke vitamina A, vitaminov kompleksa B, vitaminov C in E ter mineralen cinka in selena.
ZDRAVLJENJE DOMA
Okužba dihal ponavadi traja od 7 do 10 dni. V tem času je najboljši način, da olajšate simptome, počitek v postelji, pitje veliko tekočin, večja vlažnost zraka ali vdihavanje pare ter zdravila proti vročini in bolečinam.
Vprašanja in odgovori
Kaj je glavni vzrok za astmo?
Pogosti sprožilci:
- Zunanji alergeni, kot so cvetni prah trav, dreves in plevelov.
- Notranji alergeni, kot so prhljaj hišnih ljubljenčkov, pršice, ščurki in plesen.
- Dražilne snovi v zraku, kot so dim, kemični hlapi in močni vonji.
- Telovadba (čeprav ljudje z dobro nadzorovano astmo lahko telovadijo)[1].
Kateri so prvi opozorilni znaki astme?
Simptomi:
- Zasoplost.
- Tiščanje v prsih ali bolečina.
- Piskajoče dihanje pri izdihu, ki je pogost znak astme pri otrocih.
Slika: resnejši in kasnejši simptomi astme

- Težave s spanjem zaradi kratkega dihanja, kašlja ali piskajočega dihanja.
- Napadi kašlja ali piskajočega dihanja, ki jih poslabša respiratorni virus, kot je prehlad ali gripa[2].
Pri kateri starosti se začne astma?
Astma se pogosto začne v otroštvu, običajno pred 5. letom starosti. Veliko otrok se sooča astmo – je najpogostejša kronična bolezen v otroštvu. Lahko povzroči, da otroci zamudijo šolo in končajo v bolnišnici.
Ali lahko rentgen prsnega koša nakaže na astmo?
Zdravniki za diagnosticiranje astme uporabljajo različne fizične in slikovne preiskave. Rentgen prsnega koša je lahko koristen za odkrivanje dodatnih stanj, ki lahko povzročajo ali poslabšajo posameznikove simptome. Vendar le na podlagi rentgenskega slikanja zdravniki ne morejo postaviti diagnoze astme.
Kako se testirate na astmo?
Glavni testi, ki se uporabljajo za pomoč pri diagnosticiranju astme, so: FeNO test – vdihnete v napravo, ki meri raven dušikovega oksida v vašem izdihanem zraku, kar je znak vnetja v pljučih. Spirometrija – pihate v napravo, ki meri, kako hitro lahko izdihnete in koliko zraka lahko zadržite v pljučih.
Kateri so 4 dejavniki, ki lahko sprožijo astmo?
Psihične težave; nekatera zdravila; slabo vreme, kot so nevihte ali visoka vlažnost; vdihavanje hladnega, suhega zraka; nekatera živila, aditivi za živila in dišave
Je astma resna bolezen?
Če so simptomi hudi, bodo ljudje z astmo morda potrebovali nujno zdravstveno oskrbo in jih lahko sprejmejo v bolnišnico na zdravljenje in spremljanje. V najhujših primerih lahko astma povzroči smrt.
Katera je zadnja stopnja astme?
Zmerno persistentna astma je napredovala faza astme. Ljudje s tem stanjem vsak dan doživljajo simptome astme. Prav tako lahko občutijo simptome vsaj eno noč na teden. Izbruhi lahko trajajo več dni[3].
Viri in reference
Vir: Družinski zdravstveni vodnik. Konvencionalno in alternativno zdravljenje, Dr. Jajo Lajovic, Založba Mladinska knjiga
1. What Causes Asthma? - https://acaai.org
2. Asthma - https://www.mayoclinic.org
3. Asthma https://www.who.int





 Facebook
Facebook
 Instagram
Instagram
 info@moja-lekarna.com
info@moja-lekarna.com

