A blood clot in a deep vein of the leg, pelvis, and sometimes even an arm is called deep vein thrombosis. This type of blood clot does not cause a heart attack or stroke. A blood clot in the veins of the lungs is called a pulmonary embolism, which can also be life-threatening. Check your risk factors.
VENOUS THROMBOSIS and PULMONARY EMBOLISM: Symptoms of venous thrombosis | Consult a doctor | Warning Signs | Risk factors - avoid them! | Symptoms of pulmonary embolism | Prevention of thrombosis | Questions and Answers| Sources/references
COAT - BLOOD CLOTS: Symptoms of clot formation | Consult with a doctor | Causes of blood clots | Treatment | Conventional Medicine | Alternative Ways | Preventing blood clots | Questions and Answers| Sources/references
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (or thrombus) forms in one or more deep veins in the body, usually in the legs. Leg pain and swelling can be the result of deep vein thrombosis. The symptoms that can generally be seen or felt in the case of deep vein thrombosis are not significant; sometimes, there are no specific noticeable symptoms.
Image: showing the consequences of deep vein thrombosis in the leg area.
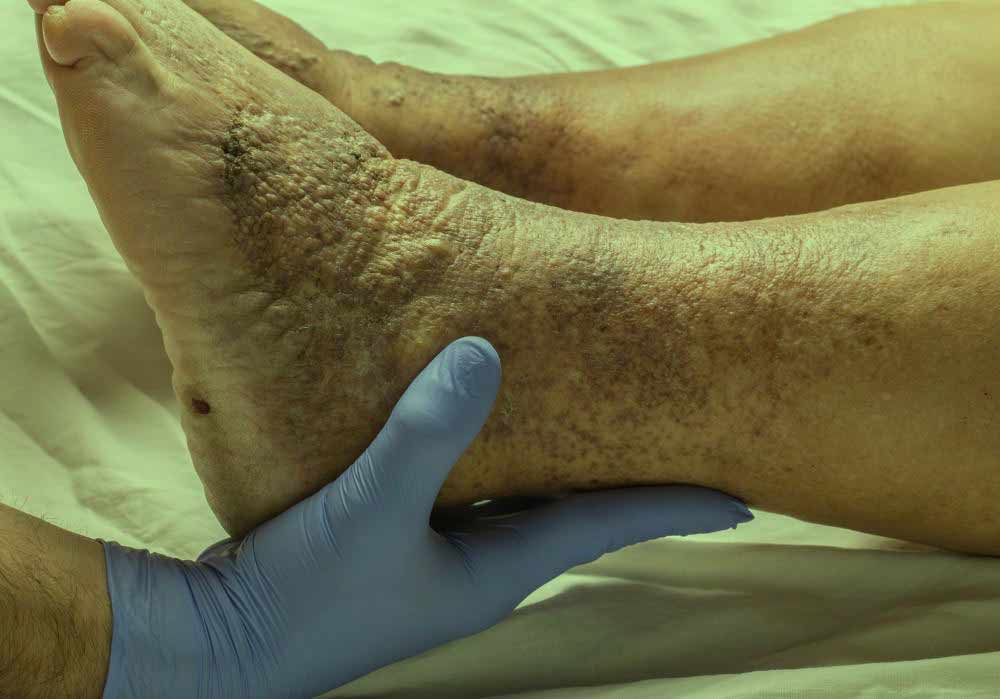
You can get this type of thrombosis if you have specific health problems that indirectly affect blood clotting. For example, a blood clot in the legs can also develop if you do not move for a long time. For example, you may not move much when traveling long distances or on bed rest due to surgery, illness, or an accident.
Deep vein thrombosis can be severe, as blood clots that sometimes form in the veins can break free. Clots can then travel through the bloodstream and get stuck in smaller pulmonary vessels, blocking blood flow through the lungs, also called a pulmonary embolism.
Video content: How does venous thrombosis occur?

When DVT and pulmonary embolism occur together in combination, such an otherwise hazardous and life-threatening condition is called venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Symptoms of venous thrombosis
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis can be as follows:
- Swelling of legs
- Pain in the leg area
- leg cramps
- pain that often starts in the swords
- change in the color of the skin on the leg - for example, a red or purple color, depending on the color of your skin
- the feeling of heat on the affected leg
Video content: symptoms, causes, and treatment of deep vein thrombosis

Deep vein thrombosis can occur without noticeable symptoms.
When should I go to the doctor?
- if symptoms of venous thrombosis appear, contact your doctor as soon as possible
- If signs of pulmonary embolism (PE) – a life-threatening complication of deep vein thrombosis – occur, seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Warning signs and symptoms of pulmonary embolism
- Sudden shortness of breath
- chest pain or discomfort that gets worse when you take a deep breath or cough
- feeling dizzy or light-headed
Video content: General about pulmonary embolism

- fainting
- rapid heartbeat
- rapid breathing
- coughing up blood
Causes of venous thromboses
Anything that prevents blood from flowing or clotting correctly can cause a blood clot to form. The leading causes of deep vein thrombosis are mainly damage to the veins - this can be due to surgery or possible inflammation of the vein, or injury due to infection.
Risk factors for venous thrombosis
Many things can increase the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
The listed risk factors are ranked lower; the more you have, the higher the risk.
Age - the older the period, the greater the chance of developing deep vein thrombosis. Nevertheless, let's not forget that this type of thrombosis can occur anytime.
Lack of movement - the biggest problem is lack of exercise and prolonged sitting, without direction, moving. This is because contraction of the muscles helps the increased amount of blood in the venous supply to move toward the heart.
Image: lack of exercise is a significant problem in modern society.

The risk of developing deep vein thrombosis increases significantly due to inactivity. A similar condition results from prolonged rest - for example, extended stay in hospital rooms and medical institutions is also problematic, especially for paralyzed people.
Operation and damaged vessels - the failure of the vessel, especially the failure of the venous valves, causes the blood to not return to the heart to a sufficient extent - the consequences are blood stagnation, reduced circulation, and, as a result, the formation of blood clots.
Pregnancy is a period of many changes in the body; among other things, the pressure in pelvic and leg veins also increases. Even six weeks after the baby's birth, the probability of the formation of clots is increased. People with a genetic predisposition are often particularly vulnerable.
Contraceptive pills - are oral contraceptives intended to implement hormone replacement therapy. The presence of such components in the blood increases the blood's ability to clot.
Excessive body weight - obesity is a severe problem in today's society, and excessive body weight also affects the pressure in the veins of the pelvis and legs.
Smoking - is a vice of modern life, which not only harms the health of your lungs but also increases the risk of venous thrombosis.
Video content: What are the risk factors for deep vein thrombosis?

Cancer - cancer diseases are diseases of the modern world - some types of cancer accelerate blood clotting, consequently increasing the risk of blood clots - and these are the reason for the increased probability of cardiovascular diseases.
Heart failure - heart failure, in particular, often increases the risk of venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. In people with significant heart failure, even a minor pulmonary embolism is cause for alarm.
Inflammatory bowel complications - especially Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis- also increase the risk of venous thrombosis.
Family history - if someone in the family has had one or even both versions of thrombotic diseases.
Genetic factors - genetic predisposition in itself will not cause the formation of blood clots; it is expressed only if other risk factors are also present.
Complications with the progression of venous thrombosis
Pulmonary embolism (PE) - PE is a potentially life-threatening complication closely related to the development of venous thrombosis. Pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot or thrombus is released from the leg area and gets stuck in the thinner veins of the lungs.
If you suffer from symptoms of a pulmonary embolism, don't wait - but contact your doctor immediately.
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism
- difficulty breathing
- unpleasant pains in the dustbin
- painful inhalation and exhalation
- faster breathing
- rapid heartbeat
- an unpleasant feeling of fainting
- coughing up blood
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism lead to further worsening of the problem, so you must react immediately and ask for medical help.
Video content: What are the symptoms of pulmonary embolism?

Clogging of veins with a clot often has adverse effects, as the clot can damage the structure of the veins - the result is usually a reduced flow through the veins. Symptoms include leg pain, leg swelling, skin discoloration, and skin sores.
Complications during treatment
Blood thinners are often used to treat deep vein thrombosis. However, bleeding while taking these effects is a worrying and unpleasant side effect. Therefore, it is essential to have regular blood tests while taking blood thinners.
Prevention of venous thrombosis
Lifestyle changes can help prevent deep vein thrombosis. Try the following strategies:
Make sure you are physically active - if you have had an operation or have been on bed rest, make sure you are mobile as soon as possible. Also, do not cross your legs when sitting, as this slows down the flow through the vascular system in the legs.
Be active during your trip - take more breaks during your trip. For example, when you are on a plane, you must stretch a little and walk to the toilet and back. If the situation does not allow it, exercise for the heels, toes, and all leg muscles. Only in this way will you ensure better blood circulation.
Don't smoke- smoking hurts your general health and well-being - including increasing the risk of DVT.
Lose excess weight - obesity is a significant risk factor for venous thrombosis of all types. Regular physical activity and exercise effectively reduce the risk of blood clots. The general goal is at least 30 minutes of physical activity every day. If you want to lose weight, maintain weight loss, or reach specific weight goals, you may need to exercise more.
CLOT - BLOOD CLOTS
SYMPTOMS
Blood clots usually do not cause any noticeable symptoms.
Image: a representation of a blood clot lodged in a vein.
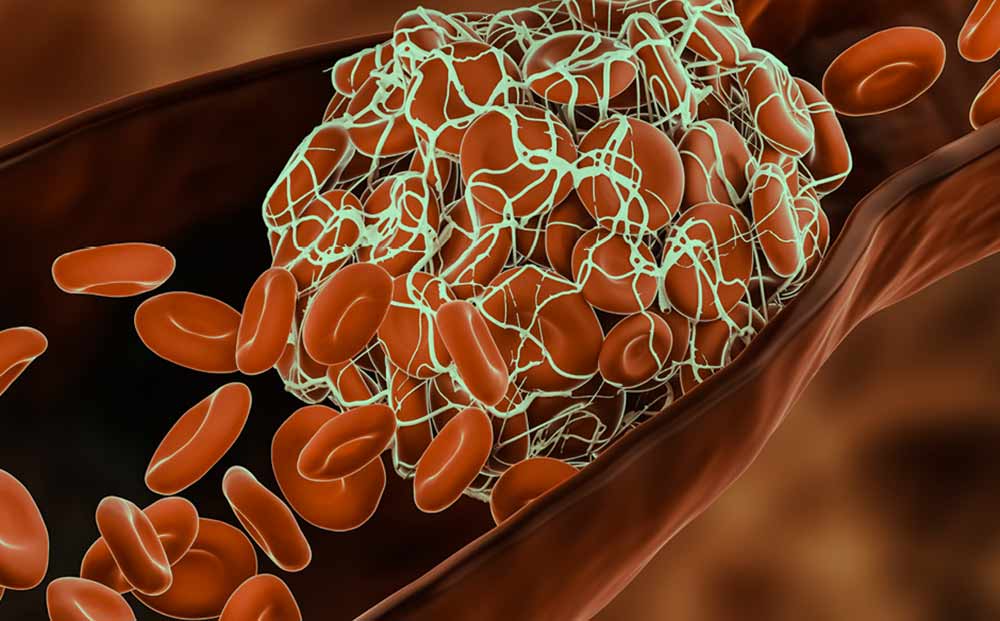
Complications from abnormal blood clots, however, can lead to various conditions and disorders:
- Sudden and isolated pain in an arm or leg, sometimes followed by skin discoloration, tingling, numbness, or a feeling of cold just below the pain site, is characteristic of a large blood clot obstructing blood circulation. If left untreated, gangrene (tissue death) can occur.
- A complex and bluish lump in a vein can be a large blood clot.
- Sudden partial or total blindness in one eye can result from a blood clot blocking a retinal artery.
- Severe dizziness or lightheadedness that makes it impossible to stand or walk may result from a small blood clot in a cerebral artery.
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR IF
- you have angina pectoris or any stroke-related symptoms. The cause may be abnormal blood clotting.
- In addition, you have a sudden or prolonged disturbance of the sensory system. Other possible reasons to be investigated include blockage of a blood vessel.
Blood flows freely through arteries as thick as a thumb and through capillaries thinner than a hair. At the first sign of injury or damage, the blood thickens or congeals and stops its flow at the site of the wound. Clotting is desirable and vital when a vessel is damaged, but clotting within a healthy vessel is abnormal and can even be life-threatening. In addition, such clots are often complications of heart disease or vein diseases such as phlebitis.
A clot that forms in the heart or blood vessel and stays there is called a thrombus. Tiny thrombi form on the walls of blood vessels to heal them, prevents damage to the vessel, and usually dissolve. But if they don't dissolve, they not only slow down the blood flow, but they can peel off or break apart and flow through the bloodstream. A clot that thus travels through the bloodstream and anchors somewhere is called an embolus. Emboli are less common than thrombi but can be much more dangerous.
The danger posed by an abnormal blood clot depends on how big it is and where it is located. A clogging clot in a cerebral artery can, for example, cause a stroke. Blood clots in the arteries that supply the heart are the leading cause of a heart attack. Tiny clots in the streets of the eye can lead to vision loss. A pulmonary embolus that blocks a pulmonary artery can cause severe breathing problems and even death.
CAUSES OF BLOOD CLOTS
As in atherosclerosis, blood clots in a vessel when the vessel is damaged or when blood flow becomes unusually slow. Diseases such as phlebitis cause inflammation of the blood vessel walls and promote the formation of abnormal clots. Clotting due to slow blood circulation is a common complication of lying down for long periods, but it can also occur with excessively long airplane flights and diving. Thrombosis of the pelvic veins is sometimes a complication of childbirth and is usually attributed to a pelvic or uterine infection.
Video content: Blood clots, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.

Abnormal clotting is sometimes associated with congestive heart muscle disease, which prevents the heart from pumping blood efficiently through circulation. In addition, blood can clot in various diseases or disorders. For example, a blood disorder called thrombocythemia causes an overproduction of platelets, tiny blood platelets that help blood clot. This, in turn, leads to excessive blood clotting. Factors that accelerate the formation of clots include smoking, birth control pills, poor diet, obesity, varicose veins, and many other diseases.
HEALING
CONVENTIONAL MEDICINE
Sometimes, they prescribe drugs that reduce the risk of abnormal blood clotting. For example, for patients at risk of developing emboli or thrombi, the doctor may prescribe acetylsalicylic acid, and streptokinase is sometimes used during intensive care to dissolve existing clots in organs such as the lungs or heart. After surgery, heparin is sometimes used to prevent clotting and deep vein thrombosis. Blood clots can be removed by surgery, but only to remove the lump; surgery is justified only in acute cases when there is a threat of tissue death.
ALTERNATIVE MODES
If you are taking anticoagulants, ask your doctor about possible contraindications before choosing herbal or vitamin therapy.
WORK WITH THE BODY
Massage therapy may be beneficial if the clot in the legs results from poor circulation. For example, if you have phlebitis, you should always be massaged by an experienced therapist for the clot to loosen from the vessel wall and enter the circulation.
HERBS
Capsicum frutescent and Ginkgo biloba are said to dissolve fibrin, a protein that is very active in clot formation. In addition, turmeric, blueberry, ginger (Zingiber officinale), grape skin extract and guggulipid, myrrh extract (Commiphora molmol) are said to reduce the sticking of platelets, garlic (Allium sativum), and onion (Allium.
BITES THAT HEAL
Vampire bat saliva, leech saliva, and copperhead viper venom sound like ingredients in a witch's concoction, but they may prove to be the solution to human life. Scientists have found enzymes in all three liquids that prevent blood clotting. Enzymes give leeches and vampire bats plenty of time to feed on their victim's blood, and snakes allow the venom to spread rapidly through the victim's bloodstream.
For us, however, synthesized versions of these enzymes may mean new antidotes against potentially harmful blood clots.
EPA) is said to serve both purposes, as does bromelain, an enzyme in pineapple.
NUTRITION
Some experts recommend a fish diet because they believe certain fish oils can make platelets less sticky. Specific vitamins and minerals can also act as natural anticoagulants. Ask your doctor about vitamin E and magnesium supplementation to prevent abnormal clotting.
PREVENTION
- eat a balanced diet low in saturated fat, fruits and vegetables, and natural fiber.
Video content: Prevention of blood clots.

- Exercise regularly to stimulate circulation and fend off extra pounds.
Some doctors recommend daily doses of acetylsalicylic acid for patients at risk of abnormal clotting. However, since this is a powerful drug, never take it regularly without consulting your doctor.
- If you are scheduled for surgery, ask your doctor about giving heparin during and after surgery. If possible, light exercises during the recovery period will promote good circulation.
Questions and answers
What are the signs of a blood clot?
- Difficult breathing.
- Irregular heartbeat - faster than normal
- pain or discomfort in the chest, which usually worsens with a deep breath or coughing.
- Coughing up blood.
- External blood pressure, dizziness, or fainting.[1]
Can a blood clot go away on its own?
Usually, your body will naturally dissolve the blood clot after, for example, an injury to a blood vessel has healed. Sometimes, however, clots form inside the veins without apparent damage or do not dissolve naturally. These situations can be hazardous and require accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
How long can you survive with a blood clot inside you?
About 25% of people with a clot will die suddenly, which will be the only symptom. About 23% of people with blood clots will die within three months of diagnosis, just over 30% will die within six months, and the mortality (death) rate one year after diagnosis is 37%.
What can dissolve blood clots quickly?
Anticoagulants such as heparin, warfarin, dabigatran, apixaban, and rivaroxaban are medicines that thin the blood and help dissolve blood clots.
How do you treat a blood clot at home?
There is no proven way to treat a blood clot at home with natural products effectively. In addition, trying to dissolve a blood clot at home can take even longer, increasing the risk of developing a potentially life-threatening condition.
What can I drink if I have a blood clot?
Moderate amounts of red wine or purple grape juice daily help prevent blood platelets from sticking together and forming clots, thanks to powerful antioxidants called polyphenols in purple grapes.
What causes venous thrombosis?
Causes of deep vein thrombosis:
- Excessive sitting - being confined to the bed
- sitting for too long without moving, for example, while traveling.
- Family history of blood clots.
- a Consequence of wearing a long-term (permanent) catheter
- obesity.
How serious is venous thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis can be a severe health problem because blood clots in deep veins can break loose, travel through the bloodstream, and become lodged in the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening and requires immediate treatment.[2]
Sources and references
Source: Family Health Guide. Conventional and alternative treatment, Dr. Jajo Lajovic, Publishing House Mladinska knjiga
1. Know the Risks, Signs & Symptoms of Blood Clots - https://www.cdc.gov
2. https://www.pennmedicine.org - Deep Vein Thrombosis