Vprašanje stranke:
Kako izgledajo oz. kako prepoznati genitalne bradavice? Vprašanje anonimne stranke
Odgovor farmacevta:
Genitalne bradavice so kožne izrastline, ki se pojavijo na spolovilih ali okoli anusa, povzročene pa so ob okužbi humanega papiloma virusa (HPV). Prepoznati jih je mogoče po značilnem videzu, vendar pa je vedno priporočljivo posvetovanje z zdravnikom za pravilno diagnozo in zdravljenje. Tukaj je podroben opis, kako izgledajo in kako jih prepoznati:
Genitalne bradavice so običajno majhne, mesnate izrastline, ki so lahko ravne ali dvignjene. Pogosto imajo grobo ali cvetači podobno površino, lahko pa so tudi gladke. Njihova barva se lahko razlikuje, včasih so rahlo rdečkaste, rožnate ali rjavkaste. Bradavice so lahko posamezne ali v skupinah, včasih tvorijo večje lezije, ki so lahko podobne grozdom cvetače.
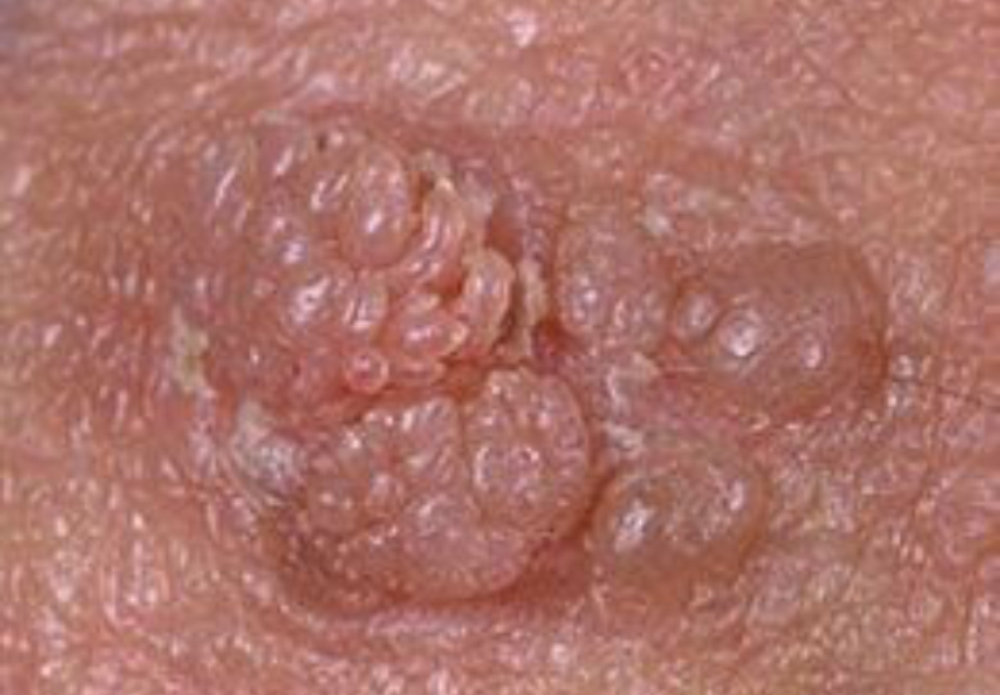
Pri moških se genitalne bradavice najpogosteje pojavijo na penisu, skrotumu, okoli anusa ali v notranjosti stegen. Pri ženskah se lahko pojavijo na predelu vulve, na stenah vagine, na materničnem vratu ali okoli anusa. Poleg tega se lahko genitalne bradavice pojavijo tudi v ustih ali v grlu po oralnem spolnem stiku z okuženo osebo.
Genitalne bradavice so pogosto neboleče, vendar lahko povzročajo nelagodje, srbenje ali pekoč občutek. V nekaterih primerih lahko prihaja do krvavitve med spolnim odnosom. Čeprav same po sebi tovrstne bradavice niso življenjsko nevarne, lahko povečajo tveganje za prenos HPV na druge osebe in povzročijo psihološki stres zaradi svojega videza.
Eden od načinov prepoznavanja genitalnih bradavic je vizualni pregled. Če opazite nenavadne izrastline na ali okoli genitalij ali anusa, je pomembno, da se posvetujete z zdravnikom. Zdravnik lahko opravi klinični pregled in po potrebi uporabi povečavo, da natančneje pregleda izrastline. V nekaterih primerih se lahko odvzame biopsija bradavice, da se potrdi diagnoza in izključi druge možne vzroke za izrastline.
Testiranje na HPV lahko pomaga pri potrditvi okužbe, čeprav ni vedno potrebno za diagnozo genitalnih bradavic. Pri ženskah lahko zdravnik opravi Papanicolaou (Pap) test, ki pomaga odkriti spremembe na celicah materničnega vratu, ki jih lahko povzroči HPV. Testiranje na visokorizične tipe HPV je lahko pomembno, saj so nekateri tipi povezani z večjim tveganjem za razvoj raka materničnega vratu.
Ali genitalne bradavice lahko zamenjamo z genitalnim herpesom?
Genitalne bradavice so majhne, mesnate izrastline, ki se pojavijo na genitalijah ali okoli anusa. Bradavice so običajno neboleče, vendar lahko povzročajo nelagodje, srbenje ali pekoč občutek. Pogosto imajo grobo ali cvetači podobno površino, lahko pa so tudi gladke. Njihova barva se lahko razlikuje od kože, včasih so rahlo rdečkaste, rožnate ali rjavkaste. Bradavice so lahko posamezne ali v skupinah. Pri moških se najpogosteje pojavijo na penisu, skrotumu, okoli anusa ali v notranjosti stegen. Pri ženskah se lahko pojavijo na vulvi, stenah vagine, materničnem vratu ali okoli anusa.
Značilni simptomi za genitalni herpes so boleči mehurčki ali razjede na genitalijah, zadnjici, notranjih stegnih ali okoli anusa. Ti mehurčki pogosto počijo in se spremenijo v boleče razjede, ki lahko trajajo nekaj tednov, preden se zacelijo. Herpes pogosto spremlja občutek srbenja, pekočega občutka ali bolečine pred pojavom mehurčkov. Prvi izbruh herpesa je običajno najhujši in ga lahko spremljajo gripi podobni simptomi, kot so zvišana telesna temperatura, utrujenost, glavobol in otekle bezgavke. Herpes je kronična okužba, kar pomeni, da virus ostane v telesu in lahko povzroča ponavljajoče se izbruhe.
Genitalne bradavice so mesnate izrastline, medtem ko so lezije herpesa mehurčki, ki se spremenijo v boleče razjede. Herpes je običajno boleč, medtem ko so bradavice večinoma neboleče. Herpes lezije se razvijajo od mehurčkov do razjed, ki se nato zacelijo, medtem ko bradavice ostanejo izrastline, dokler niso odstranjene ali zdravljene. Herpes lahko povzroči gripi podobne simptome, kar ni značilno za genitalne bradavice.
Zanimivo branje: Svečke za odvajanje blata
Zanimivo branje: Anogenitalne bradavice







 Facebook
Facebook
 Instagram
Instagram
 info@moja-lekarna.com
info@moja-lekarna.com

