Pljučnica je resna okužba dihal, ki povzroči vnetje alveolov v enem ali obeh pljučnih krilih. Alveoli (zračni mešički) se posledično lahko napolnijo s tekočino ali gnojem, kar povzroči kašelj s sluzjo ali gnojem, kateremu ponavadi sledi še vročina, mrzlica in težko dihanje. Različni organizmi, vključno z bakterijami, virusi in glivicami, lahko povzročijo pljučnico. V veliko pomoč pa vam bo tudi prispevek o pljučnem raku, plevritisu in astmi.
PLJUČNICA: Simptomi pljučnice | Posvet z zdravnikom | Vzroki pljučnice | Diagnostični postopki | Zdravljenje | Konvencionalna medicina | Alternativni načini | Prehrana | Zdravljenje doma | Vprašanja in odgovori | Viri/reference
PLJUČNI RAK: Simptomi pljučnega raka | Posvet z zdravnikom | Vzroki pljučnega raka | Zdravljenje | Konvencionalna medicina | Dopolnilno zdravljenje | Preprečevanje | Vprašanja in odgovori | Viri/reference
PLEVRITIS: Simptomi plevritisa | Posvet z zdravnikom | Vzroki plevritisa | Zdravljenje | Diagnostični postopki | Konvencionalna medicina | Alternativno zdravljenje | Vprašanja in odgovori | Viri/reference
ASTMA: več na voljo na povezavi Več o astmi
Pljučnica je vnetje v pljučih, ki ga povzročajo različne virusne in bakterijske okužbe ali kemični dejavniki. Pljuča se odzovejo tako, da se v njih nabirajo tekočina in celice, ki preidejo iz okvarjenega tkiva. Če je vnetje omejeno na en reženj pljuč, jo opredelimo kot reženjsko (lobarno) pljučnico; vnetje, ki se iz sapnic širi v druge dele enega ali obeh pljučnih kril, imenujemo bronhopnevmonija.
Če sta vneti obe pljučni krili, stanje imenujemo obojestranska pljučnica. Pljučnica ponavadi traja okoli dva tedna, odvisno od vašega splošnega zdravja, čeprav se lahko še mesec ali dlje po ozdravitvi počutite izčrpani.
Slika: pljučnica - zahtevna bolezen.
Virusna pljučnica je ponavadi blaga. Potem, ko je zdravnik postavil diagnozo, se lahko zdravite doma.
Bakterijska pljučnica je bolj zapletena in nevarnejša. Do odkritja antibiotikov so bolniki pogosto umirali; nevarna je še danes, zlasti za starejše.
Še leta 1976 je v ZDA zaradi legionarske bolezni umrlo 29 ljudi, preden so jo prepoznali in zdravili kot bakterijsko pljučnico. Med mnogimi drugimi oblikami pljučnice omenimo atipično pljučnico, ki je najpogostejša pri otrocih in mladih odraslih.
Simptomi pljučnice - znaki
- kombinacija vročine in mrzlice, bolečin v mišicah, utrujenosti, povečanih vratnih bezgavk, prsne bolečine, vnetega žrela in kašlja je značilna za virusno pljučnico.
- kombinacija visoke vročine, kašlja z gostim rumeno-zelenim izpljunkom, ki lahko vsebuje kri, težkega dihanja, hitrega dihanja, ostre prsne bolečine, ki se poslabša med globokim dihanjem, trebušnih bolečin in hude utrujenosti je simptom bakterijske pljučnice.
Video vsebina: Pljučnica - simptomi in diagnostika

- izguba apetita in hujšanje, vročina, kašelj z izpljunkom - morda po obdobju nezavesti - so lahko znaki aspiracijske pljučnice.
- pri otrocih so glavni znaki pljučnice: naporno in hitro dihanje (več kot 45 vdihov na minuto), nenadna vročina, kašelj, piskanje in modrikasto obarvana koža.
Posvetujte se z zdravnikom, če:
- simptomi kažejo na to, da imate katero koli od oblik pljučnice. Potrebujete takojšnje zdravljenje, da boste okrevali in se izognili zapletom,
- se po postavitvi diagnoze in predpisanem zdravljenju ostra bolečina v prsih ne izboljša; vedno težje dihate; nohti ali koža potemnijo ali se modrikasto obarvajo.
V pljučih se ne izmenjuje dovolj kisika in potrebujete zdravniško pomoč,
- izkašljate kri; morda potrebujete dodatno zdravljenje, ker se je okužba poslabšala.
DOKAZI OKUŽBE
Slika: primerjava zdravega bronhiola in takšnega s tekočino.

V zdravih pljučih se ogljikov dioksid iz krvi zamenja za kisik skozi majhne zračne vrečke, imenovane pljučni mešički ali alveole (v okvirju, zgoraj). Okužba pljuč, ki jo povzročajo bakterije, virusi ali kemični dejavniki, povzroči, da tkivo v pljučnih mešičkih oteče in se napolni s tekočino (v okvirju, spodaj). Pogost znak pljučnice je plitvo, naporno dihanje zaradi nezadostne oskrbe s kisikom.
Pljučnica je pogosto zaplet drugih bolezni in se lahko, tako kot prehlad ali gripa, prenaša s človeka na človeka. Bolniki, ki se zdravijo v bolnišnici zaradi drugih težav, lahko zbolijo za bakterijsko pljučnico, ki je odporna na običajno antibiotično zdravljenje. Bakterijske pljučnice zunaj bolnišnic so ponavadi manj hude in se dobro odzovejo na antibiotike.
VZROKI
Virusno pljučnico povzročajo mnogi pogosti virusi. Bakterijsko pljučnico najpogosteje povzroča Streptococcus pneumoniae, imenovan tudi pnevmokok. Bakterija Hemophilus intluenzae povzroča pljučnico, ki se razvije kot zaplet gripe. Pljučnica je spet vse pogosteje posledica okužbe z bakterijami tuberkuloze. Bakterije vrste Legionella povzročajo legionarsko bolezen. Ta m podobne pljučnice se prenašajo z okuženo vodo, mdr. iz pip za vročo vodo in prezračevalnih naprav.
Video vsebina: vzroki pljučnice

Aspiracijska pljučnica nastane, če pridejo v pljuča bakterije iz ust ali želodca, ponavadi med spanjem, nezavestjo ali epileptičnim napadom. Te bakterije se normalno nahajajo v prebavilih zdravih ljudi. Mala količina vdihane sluzi večini ljudi ne škodi, lahko pa povzroči pljučnico pri alkoholikih ali drugih ljudeh z oslabljenim imunskim sistemom. Bakterije pridejo v pljuča tudi zaradi nenamernega vdihovanja izbruhane vsebine, ponavadi med nezavestjo.
Pnevmocistna pljučnica se razvije, če je imunska obramba telesa izčrpana zaradi aidsa, Hodgkinove bolezni ali drugih bolezni, ki okvarjajo imunski sistem. Pri več kot polovici bolnikov z aidsom se razvije kot sekundarna okužba, vendar obstaja učinkovito zdravljenje.
DIAGNOSTIČNI POSTOPKI
Pljučnice se lahko kažejo od blagega stanja, ki ga lahko zdravite doma, do življenjsko nevarne okužbe, ki jo je treba zdraviti v bolnišnici. Zato potrebujete strokovno diagnozo, da si zagotovite ustrezno zdravljenje in uspešno okrevanje.
OPOZORILO - POSTURALNA DRENAŽA
Da odstranite sluz iz pljuč, poskusite posturalno drenažo od 5 do 15 minut trikrat na dan. Tehnika je telesno zahtevna, zato naj jo odobri zdravnik. Vselej jo izvajajte ob podpori drugega človeka.
Lezite na posteljo z zgornjo polovico telesa preko roba, z rokami se podprite na tleh. Izkašljajte sluz globoko iz pljuč in jo izpljuvajte v posodo na tleh. Na koncu odplaknite sluz v stranišče.
Če vam je ta tehnika prenaporna, naj prijatelj ali družinski član z ukrivljenimi dlanmi več minut nežno udarja po zgornjem delu hrbta, da se odluščijo izločki v pljučih.
Zdravnik bo najprej poslušal prsni koš, da odkrije nenavadne poke, in ga pretipal, da odkrije zamolkline, ki kažejo na nabiranje tekočine v pljučih. Če je treba, lahko diagnozo potrdi z rentgenskim slikanjem, ki prikaže, kje so pljučni zračni mešički, napolnjeni s tekočino in celičnimi ostanki. Vzorce krvi in sputuma (izpljunka) - ki jih včasih dobijo tako, da v pljuča skozi sapnik vstavijo inštrument - lahko preiščejo na mikroorganizme, vendar rezultati niso vedno prepričljivi.
ZDRAVLJENJE
Cilj zdravljenja pri vseh oblikah pljučnice je hitro okrevanje, ker se lahko razvijejo zapleti, če bolezen traja dalj časa. Pri vsakem zdravljenju je potreben počitek v postelji. Konvencionalna medicina se osredotoča na ozdravljenje okužbe, z alternativnimi načini zdravljenja pa lahko olajšate neprijetne simptome.
KONVENCIONALNA MEDICINA
Pri večini oblik pljučnice sta glavna ključa do okrevanja počitek v postelji in »produktivni kašelj« - izkašljati morate sluz in drugo tekočino iz pljuč.
Video vsebina: zdravljenje in preventiva - pljučnica

Če imate blago obliko virusne pljučnice, najpogosteje lahko okrevate doma. Da zmanjšate vročino in bolečino, vzemite acetilsalicilno kislino ali paracetamol, pijte veliko tekočine in jejte lahko hrano. Če imate bakterijsko pljučnico, vam bo zdravnik predpisal antibiotik, npr. penicilin ali eritromicin. Ostati morate v postelji, dokler se vročina ne zniža in postane dihanje normalno. Če so pljuča močno napolnjena s tekočino, boste morda potrebovali kisik ali vas bodo morali začasno priključiti na respirator - zato vas morajo sprejeti v bolnišnico. Pri aspiracijski pljučnici so skoraj vedno potrebni intravenski antibiotiki in daljše zdravljenje v bolnišnici. Pnevmocistno pljučnico zdravijo s počitkom v postelji, antibiotiki, pentamidinom ali sulfametoksazolom in trimetoprimom, in dekongestivi, ki zmanjšajo količino tekočine v pljučih.
Za mnoge vrste bakterijske pljučnice so na voljo cepiva, še več jih razvijajo. Cepljenje proti pljučnicam priporočajo vsem nad starostjo 65 let in bolnikom s kroničnimi pljučnimi boleznimi, srpastocelično anemijo, srčnimi boleznimi, alkoholikom, bolnikom z boleznimi imunske pomanjkljivosti, kot je aids, in tudi ljudem, ki imajo poškodovano ali odstranjeno vranico. Na voljo so tudi cepiva za nekatere oblike gripe. Priporočajo jih starejšim ljudem.
PAZITE SE PTIČJIH KLETK
Papige prenašajo psitakozo - redko obliko pljučnice - na svoje človeške lastnike, ne da bi ti kaj sumili. Bolne ptice razširjajo mikroorganizme s prahom njihovega perja, izločki in celo pri ugrizu v prst. Simptomi psitakoze so vročina, mrzlica, glavobol, bolečine v mišicah, izguba teka, slabost, bruhanje in povečana vranica.
Cepivo proti gripi vas bo zaščitilo ali pred boleznijo samo ali pred tem, da bi se razvila huda oblika, ki bi lahko povzročila zaplete, kot je pljučnica.
ALTERNATIVNI NAČINI
Video vsebina: 6 povsem naravnih načinov za infekcije v predelu prstnega koša

Če imate pljučnico, lahko s številnimi alternativnimi zdravili olajšate simptome in pospešite okrevanje.
AKUPUNKTURA
Akupunktura na pljučnem meridianu pospeši okrevanje tako, da izboljša kašelj in zmanjša nabiranje tekočine v pljučih, izboljša vaše počutje in dvigne energijsko raven. Ključne točke so P7 za izkašljevanje snovi iz pljuč, P5 za umiritev kašlja in P1 za odstranjevanje tekočine iz pljuč. Glede na potek bolezni lahko akupunkturist poskuša tudi spodbuditi imunski sistem.
AROMATERAPIJA
Okrevanje pri pljučnici lahko pospešite, če v toplo kopel ali inhalator dodaste eterična olja evkaliptusa (Eucalyptus globulus), sivke (Lavandula officinalis), čajevca (Melaleuca spp) ali bora. Če imate astmo, ne inhalirajte pare, ker lahko razdraži pljuča.
DELO S TELESOM
Ko izgine vročina, lahko z masažo mišic zgornjega dela hrbta zmanjšate nabiranje tekočine v pljučih. Če dodaste masažnemu olju nekaj kapljic eteričnega olja evkaliptusa (Eucalyptus globulus), se bo sluz v pljučih zmehčala in lažje izločila.
ZELIŠČA
Pomemben del procesa zdravljenja je, da se pljuča očistijo sluzi, zato pri okrevanju pomagajo tradicionalna zeliščna sredstva za izkašljevanje. Sami si pripravite sredstvo za izkašljevanje tako, da zmešate 60 g sladkega korena (Glycyrrhiza glabra), 30 g skorje pozne čremse (Prunus serotina), 30 g lapuha (Tussilago farfara), 4 g lobelije (Lobelia inflata) in 30 g črne mete (Marrubium vulgare).
Video vsebina: 5 zelišč za zdravje pljuč

Eno žlico mešanice 5 minut vrite v skodelici vode; pustite stati 10 minut, nato jo precedite v čisto posodico. Odrasli naj bi popili skodelico vsaki dve uri. Lobelija je lahko strupena, zato je nikoli ne uživajte več, kot je priporočeno. Če vam postane slabo, nehajte uživati to mešanico.
ČEBULNO ZDRAVILO
Poskusite doma pripravljen sirup proti kašlju, ki kombinira pomirjujoč učinek medu z ostrim pridihom surove čebule. Med prelijte preko rezin surove bele čebule in pustite stati preko noči v pokriti posodi. Zjutraj mešanico precedite v čisto posodo in izločite rezine čebule. Vsake štiri ali šest ur vzemite žlico mešanice, najbolje je, če jo prej malo ogrejete.
Nikoli je ne dajajte otrokom ali nosečim ženskam.
Pri pljučnici priporočajo prevretek svilnice (Asclepias tuberosa). Eno žlico zelišča 10 minut vrite v skodelici vode, pustite stati 5 minut in precedite; pijte štiri ali petkrat na dan.
Telesu pomagate premagati okužbo, če jeste surov česen (Allium sativum) ali vzamete tri kapsule česna trikrat na dan. Echinaceja (Echinacea spp) pomaga pri okrevanju po okužbi. Pripravite jo lahko kot čaj - 1 čajna žlička v skodelici vode - in uživate trikrat na dan, jemljete 30 kapljic tinkture štirikrat na dan ali jemljete kapsule po priloženih navodilih.
HOMEOPATIJA
Nekatera priporočena zdravila v prosti prodaji so: bryonia, phosphorus in arsenicum album; držite se priloženih navodil.
PREHRANA
- V boju proti okužbi zelo pomaga vitamin C, do 1000 mg na uro, če ga začnete jemati v dveh dneh po začetku bolezni. Če se pojavi driska/ zmanjšajte odmerek.
- Dihalni in imunski sistem spodbujate z od 25000 do 50000 IE vitamina A na dan, ne več kot dva tedna.
- Tudi dodatki cinka, do 60 mg na dan, pomagajo imunskemu sistemu premagati okužbo.
- 600 IE vitamina E na dan dobro deluje na poškodovano pljučno tkivo.
- Če jemljete antibiotike pri bakterijski pljučnici, jemljite dodatke Lactobacillusa acidophilusa v obliki kapsul ali kultur v jogurtu, da nadomestite koristne črevesne bakterije.
ZDRAVLJENJE DOMA
- Bolečine v prsnem košu lahko zmanjšate s toplimi obkladki na prsih ali hrbtu za 10 minut večkrat na dan. Termofor ali grelno blazino zavijte v brisačo, da preprečite opekline.
Video vsebina: 3 preprosti domači pripravki v primeru pljučnice

- Poskusite tradicionalne tople gorčične obkladke, s katerimi zmehčate sluz v pljučih. Posušena zmleta gorčična zrna zmešajte s toliko tople vode, da nastane gosta krema. Namažite jo na tanko krpo, prepognite in za nekaj minut položite na prsni koš, vendar ne pretiravajte: gorčica povzroča mehurje, če jo predolgo pustite neposredno na koži.
- Pijte obilo tekočine in svežih sadnih in zele-njavnih sokov, da se izločki v pljučih razredčijo in jih lažje izkašljate.
PLJUČNI RAK
V zgodnjem stadiju ponavadi pljučni rak ne povzroča nobenih težav.
Slika: izgled začetnega žarišča pljučnega raka

Ko se simptomi začnejo pojavljati, nastanejo zaradi zapore dihalnih poti ali širjenja raka v druge dele telesa.
SIMPTOMI
- kroničen, suh, grob kašelj, včasih s krvavim izpljunkom - t. i. kadilski kašelj;
- ponavljajoče se okužbe dihal, npr. bronhitis ali pljučnica;
- težko dihanje, piskanje med dihanjem, dolgotrajna bolečina v prsih; hripavost;
- otekanje vratu ali obraza;
- bolečine in šibkost v rami, roki ali dlani;
- če se je rak razširil izven pljuč: oslabelost, utrujenost, hujšanje, izguba teka, prekinjajoča se (intermitentna) vročina, hudi glavoboli, bolečine po telesu.
POSVETUJTE SE Z ZDRAVNIKOM, ČE
- opazite simptome, značilne za pljučnega raka, posebej kronični kašelj, krvav izpljunek, piskanje med dihanjem, hripavost ali ponavljajoče se okužbe dihal. Zdravnik naj temeljito pregleda vaša dihala.
Pljučni rak je v zahodnem svetu glavni vzrok smrti zaradi raka, hkrati pa se ga da najbolje preprečiti. Vsaj 4 od 5 primerov so povezani s kajenjem - dokazana je bila vzročna povezava.
V 20. letih je mnogo moških začelo kaditi cigarete, najbrž zaradi večje reklame. Čez dvajset let je pogostnost pljučnega raka strmo narasla. V 40. letih je začelo kaditi precej več žensk. Čez dvajset let je podobno strmo narasla pogostnost pljučnega raka pri ženskah.
Pljučni tumor skoraj vedno vznikne v gobastih, rožnato-sivih stenah sapnic oz. bronhijev - cevastih, razvejanih dihalnih poti v pljučih. Ločimo več kot 20 različnih vrst malignih tumorjev, ki izvirajo iz pljuč, t. i. primarnih pljučnih rakov. Glavni vrsti sta drobnocelični in nedrobnocelični bronhialni karcinom. Pogostejše različice nedrobnoceličnega raka so ploščatocelični karcinom, adenokarcinom in velikocelični karcinom.
Video vsebina: kaj je pljučni rak?

Ploščatocelični karcinom navadno vznikne v celicah osrednjih sapnic, največjih vej bronhialnega vejevja. Je najpogostejša vrsta pljučnega raka pri moških in pri kadilcih. Najlažje ga zgodaj odkrijemo, ker najdemo njegove celice že zgodaj s preiskavo vzorcev sputuma (izpljunka). Hkrati se tudi najbolje odzove na zdravljenje, ker se sorazmerno počasi širi.
Adenokarcinom - najpogostejša vrsta raka pri ženskah in nekadilcih - ponavadi nastane na obrobju pljuč v majhnih bronhih ali še manjših hronhiolih. Pogosto se razširi v prostor med pljuči in prsno steno. Zaradi mesta nastanka ga težje zgodaj odkrijemo.
Velikocelični karcinomi so skupina rakov z velikimi celicami nenormalnega izgleda, ki izvirajo iz obrobja pljuč. Med nedrobnoceličnimi bronhialnimi karcinomi so najmanj pogosti.
Drobnocelični karcinom je najbolj agresivna oblika pljučnega raka. Imenujejo ga tudi rakov senec, ker so celice pod mikroskopom podobne ovsenim zrnom. Tako kot ploščatocelični karcinom vznikne v osrednjih bronhih. Hitro se širi, ponavadi še preden se pojavijo simptomi, zato je zelo nevaren.
V ZDA vsako leto pri več kot 170 000 ljudeh postavijo diagnozo pljučnega raka, večina jih je med 40. in 70. letom starosti. Le 1 % bolnikov s pljučnim rakom je mlajših od 30 let in le okoli 10% jih je starejših od 70. Petletno preživetje se izboljšuje - trenutno preživi pet let 15% bolnikov s pljučnim rakom. Napoved poteka bolezni pri posamezniku je odvisna od vrste raka, njegovega splošnega zdravja in razširjenosti raka ob času diagnoze.
VZROKI
Tako kot pri raku nasploh vpliva na nagnjenost k pljučnemu raku dedni zapis. Dejstvo, da se pljučni rak pojavlja v nekaterih družinah, kaže, da je nagnjenost podedovana. Razen tega so prepoznali določene genetske napake, ki povzročijo, da so nekateri ljudje bolj občutljivi za karcinogene v cigaretnem dimu.
Slika: na sliki so navedeni vzroki, ki vodijo v razvoj pljučnega raka.

Vendar pa ima vsak, ki pokadi škatlico cigaret na dan, v primerjavi z nekadilcem 20-krat večjo možnost, da bo zbolel za pljučnim rakom. Pri ljudeh, ki pokadijo več kot dve škatlici na dan, se tveganje potroji. Če prenehate kaditi, se tvega-
TUMOR V PLJUČIH
Pljučnega raka ponavadi ne odkrijemo, dokler se ne pojavijo simptomi in ne opravimo rentgenskega slikanja. Ploščatocelični karcinom in adenokarcinom sta najpogostejši vrsti. Ploščatocelični karcinom ponavadi nastane v osrednjih bronhih. Adenokarcinom najdemo v manjših bronhiolih.
nje pomembno zmanjša, vendar pa so bivši kadilci še vedno bolj občutljivi kot nekadilci. Tudi pasivno kajenje povzroča pljučnega raka, zato imajo nekadilci, ki živijo ali delajo s kadilci, nekoliko večje tveganje, da zbolijo za pljučnim rakom, kot tisti, ki živijo v nekadilskem okolju.
Pljučnega raka lahko povzročijo tudi drugi karcinogeni, če jih sčasoma inhalirate veliko količino. Vendar imajo strokovnjaki različno mnenje o tem, kako škodljiva je izpostavljenost določenim karcinogenom.
Delavci, ki so dnevno izpostavljeni azbestu, siliciju, mineralnemu in premogovemu prahu, arzeniku ali radioaktivnemu plinu radonu, so bolj nagnjeni k nastanku pljučnega raka kot povprečen posameznik, še posebej, če so kadilci.
Tumor najraje vznikne v pljučnem tkivu v brazgotinah, nastalih po okužbah ali boleznih, npr. tuberkulozi ali sistemski sklerozi. Ker se pljučni rak pogosto pojavi pri ljudeh, ki jedo veliko maščob in holesterola, nekateri raziskovalci sumijo, (Ja tudi prehrana vpliva na tveganje za pljučnega raka.
DIAGNOSTIČNI POSTOPKI
Če zdravnik pri rutinskem pregledu najde povečane bezgavke nad ključnico ali tvorbo v trebuhu, sliši šibko dihanje ali nenormalne dihalne zvoke v pljučih ali najde zamolklino pri pretrkavanju prsnega koša, bo posumil na pljučnega raka. Pri nekaterih vrstah pljučnega raka so v krvi nenormalno visoke koncentracije določenih hormonov ali snovi, kot je kalcij.

Če se pri bolniku pojavijo ti znaki in ni drugega možnega vzroka, zdravnik posumi na pljučnega raka.
Ko začne tumor povzročati simptome, se ponavadi že vidi na rentgenski sliki. Včasih odkrijejo tumor, ki še ni začel povzročati simptomov, na rentgenski sliki, narejeni iz drugih razlogov. Za podrobnejše podatke opravijo slikanje z računalniško tomografijo (CT) prsnega koša.
Rakaste celice lahko odkrijejo s preiskavo izpljunka ali izpirka pljuč, diagnozo pa potrdijo z biopsijo. Blago anesteziranemu bolniku uvede zdravnik tanko optično cev skozi nos v dihalne poti do mesta tumorja, kjer odščipne majhen košček tkiva. Če z biopsijo raka potrdijo, z drugimi preiskavami določijo njegovo vrsto in razširjenost. Bližnje bezgavke pregledajo na rakaste celice, s slikovnimi preiskavami, npr. CT ali kostno scintigrafijo, pa odkrivajo zasevke po telesu.
Preiskava sputuma in rentgensko slikanje pljuč nista dovolj učinkovita za odkrivanje majhnih tumorjev, značilnih za zgodnji stadij pljučnega raka. Zato rednega vsakoletnega rentgenskega slikanja za odkrivanje pljučnega raka ne priporočajo.
ZDRAVLJENJE
Če lahko tumor uspešno kirurško odstranijo, ima bolnik odlične možnosti za vsaj enoletno preživetje, in več kot 50% možnost, da bo živel vsaj pet let. Izziv je torej, da pljučnega raka prepoznamo tako zgodaj, da je kirurška odstranitev še mogoča.
KONVENCIONALNA MEDICINA
Odločitev za kirurški poseg ne temelji samo na vrsti pljučnega raka, ampak tudi na razširjenosti in bolnikovem splošnem zdravju. Mnogi bolniki s pljučnim rakom - posebej kadilci - imajo tudi pljučne ali srčno-žilne bolezni, ki operacijo izključujejo. Rak, ki se je razširil na bezgavke med pljučnima kriloma, je včasih veljal za neoperabilnega. Danes pa s kombinacijo operacije s pred in pooperativno kemoterapijo in obsevanjem dosegajo dobre uspehe.
Video vsebina: pljučni rak - zgodnja diagnoza in zdravljenje

Če je možna, je za nedrobnocelični karcinom operacija najboljši način zdravljenja. Pred posegom poskušajo velikost tumorja zmanjšati z obsevanjem in kemoterapijo. Med operacijo kirurg odstrani tumor skupaj z okoliškim pljučnim tkivom in bezgavkami; včasih mora odstraniti celo pljučno krilo. Po operaciji bolniki dalj časa ostanejo v bolnišnici. Za lajšanje pooperativne bolečine dobivajo analgetike. Včasih je potrebno še obsevanje, da se uničijo preostale rakave celice; ponavadi ga odložijo vsaj za mesec dni, da se operativna rana pozdravi. Nedrobnocelični karcinom, ki ga ne morejo operativno odstraniti, zdravijo z obsevanjem.
Drobnocelični karcinom zdravijo s kombinacijsko kemoterapijo - z več kot enim zdravilom - pogosto skupaj z obsevanjem, ker se hitro širi. Pri izbranih bolnikih predlagajo zdravniki presaditev kostnega mozga, da lahko uporabijo višje odmerke kemoterapije.
Slika: izgled drobnoceličnega karcinoma pod mikroskopom.
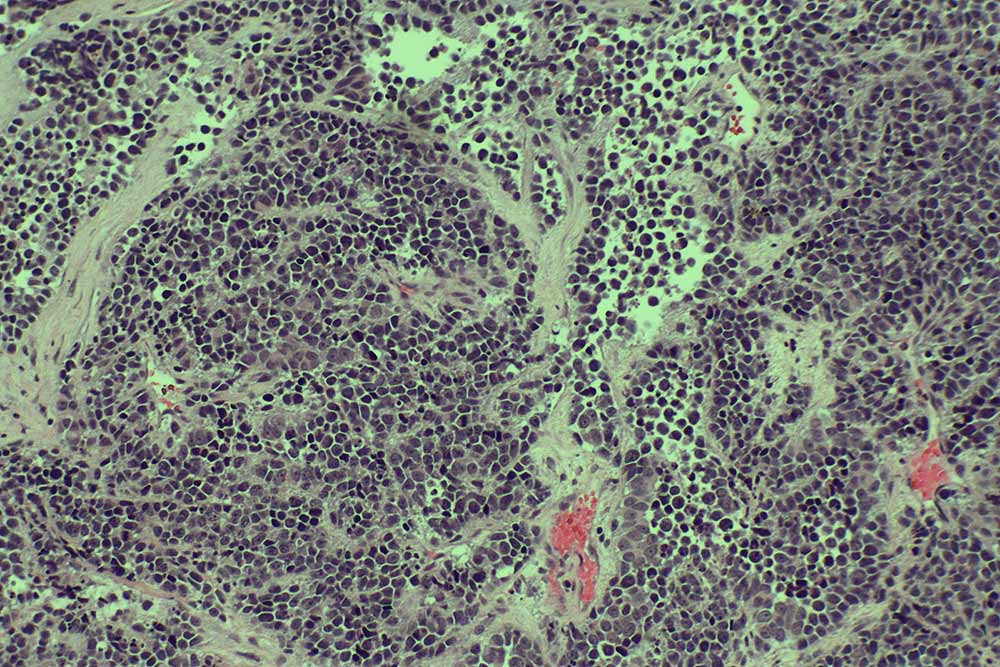
Bolnike, pri katerih se je rak že razširil na oddaljena mesta, zdravijo s kemoterapijo ali obsevanjem. Pljučnega raka z zasevki je izjemno težko ozdraviti, zato je glavni cilj zdravljenja lajšanje težav in podaljšanje življenja. Z današnjim zdravljenjem lahko tumor zmanjšajo, kar zmanjša bolečine in odpravi druge simptome. Bolniki z napredovalim pljučnim rakom potrebujejo zdravila za lajšanje bolečine. Največ uporabljajo morfij in njegove derivate, ki učinkovito obvladajo bolečino pri raku.
Raziskovalci stalno iščejo nove načine, kako ozdraviti pljučnega raka, lajšati simptome in izboljšati kakovost življenja. Preizkušajo nove kombinacije v kemoterapiji, nove oblike obsevanja in zdravila, ki napravijo rakave celice bolj občutljive za obsevanje. Z eksperimentalnimi laserskimi posegi so učinkovito odstranili tumorje, ki so zapirali sapnice, in s tem izboljšali dihanje. Raziskujejo tudi različne oblike imunskega in genskega zdravljenja pljučnega raka. Imunsko zdravljenje spreminja odziv imunskega sistema v upanju, da se bo bolj agresivno boril proti rakavim celicam; gensko zdravljenje pa vgrajuje v tumorske celice tuj genski material, da bi zaustavil ali upočasnil njihovo razmnoževanje.
DOPOLNILNO ZDRAVLJENJE
Medtem ko poteka konvencionalno zdravljenje, lahko na mnogo načinov olajšamo bolečino, strah in slabo počutje, povezano z rakom. Dopolnilno zdravljenje lahko večinoma varno izvajamo ob konvencionalnem, vendar pa ga nikoli ne smemo uporabljati kot zamenjavo za zdravniško oskrbo. Rezultati dopolnilnega zdravljenja se med bolniki razlikujejo. Mnogim so koristile podporne skupine, izboljšanje prehrane, različ-
TVEGANJE ZARADI RADONA
Radon je radioaktiven plin brez barve in vonja, ki stalno izhaja iz Zemljine skorje. Raziskave rudarjev v rudniku urana na koloradski planoti v 50. letih so jasno pokazale, da dolgotrajna, velika izpostavljenost radonu povzroča pljučnega raka. Ameriška agencija za varstvo okolja (EPA) opozarja, da izpostavljenost radonu v dozi 4 pCu ali več lahko povzroči pljučnega raka. (PikoCurie - pCu - je bilijonina Curieja, standardne enote za merjenje radioaktivnosti.) Posebej kadilci so izpostavljeni tveganju zaradi radona tudi v majhnih dozah.
Video vsebina: povezava radioaktivnega radona in pljučnega raka.

Ameriška agencija za varstvo okolja predlaga, da se v vseh ameriških domovih določi sevanje radona in uvedejo varnostni ukrepi. Nasprotniki te kampanje trdijo, da stroški tega preizkušanja niso upravičeni, zagovorniki pa trdijo, da dokazi - ne glede na to, kako posredni so - kampanjo upravičujejo. Dejstvo je, da le malo znanstvenih dognanj podpira trditve EPA; v nekaterih raziskavah so celo dokazali, da je v državah z največjim sevanjem radona v gospodinjstvih pogostnost pljučnega raka manjša kot povprečna.
Agencija na te dokaze odgovarja: »Bolje previdnost kot obžalovanje.«
ne metode dela s telesom in metode medicine duha in telesa.
PREHRANA
Raziskave prehrane so pokazale, da nekateri vitamini in minerali varujejo pred nastankom pljučnega raka. Antioksidanti, mdr. vitamina C in E, beta karoten (vitamin A) in nekateri karotenoidi naj bi pljuča varovali pred škodljivimi učinki tobačnega dima in drugih karcinogenov. Vendar pa navdušenje nad vitamini zmanjšujejo druge raziskave, ki zaščitnih učinkov niso dokazale ali celo trdijo nasprotno.
Dokler ne bo opredeljena njihova natančna vloga, večina raziskovalcev ne svetuje dodatkov vitaminov in mineralov za preprečevanje pljučnega raka. Raje predlagajo uravnoteženo prehrano, ki zagotavlja dovolj vlaknin in potrebnih hranil.
NEGA DOMA
Po operaciji pljuč vas lahko zdravnik ali medicinska sestra naučita vaj za izboljšanje dihanja in krepitev mišic prsnega koša. Razdraženo kožo po obsevanju zaščitite tako, da nosite ohlapna oblačila in se izogibate soncu. Ne uporabljajte losjonov, razen če to odobri vaš zdravnik.
PREPREČEVANJE
Najboljša zaščita pred pljučnim rakom je, da ne kadite. Prenehati kaditi je težko, vendar ni nemogoče. (Glejte geslo Nikotin, odtegnitev.) Medtem ko se pripravljate, da boste prenehali, zmanjšajte število pokajenih cigaret. Mnogo ljudi pa trdi, da je bolj učinkovito prenehati naenkrat kot počasi »zmanjševati«. Pridružite se podporni skupini, ki vas bo podprla v vaši odločitvi, da nehate. Če živite ali delate s kadilci, jih spodbujajte, naj nehajo kaditi, in jih prosite, naj v vaši prisotnosti ne kadijo. Če ste na delovnem mestu izpostavljeni kemičnim karcinogenom, upoštevajte varnostne ukrepe.
PLEVRITIS
SIMPTOMI
Plevritis:
- huda, ostra, minljiva bolečina v prsnem košu, lahko samo na eni strani, ko globoko dihate, kašljate, se premikate ali kihate;
Slika: prikaz plevritis-a.
- huda bolečina, ki izgine, ko zadržite dih.
Plevralni izliv:
- težko dihanje;
- suh kašelj.
POSVETUJTE SE Z ZDRAVNIKOM, ČE
- občutite zgornje simptome, posebej če bolezen še ni bila opredeljena; plevritis in plevralni izliv sta znaka resnih bolezni, kot sta pljučnica in pljučni rak.
- zgornje simptome spremlja vročina, tudi če je nizka. Možno je, da imate vrsto okužbe, imenovano empiem, pri kateri je potrebno zdravljenje z antibiotiki.
Plevritis je vnetje plevre - vlažne, dvoplastne opne, ki ovija pljuča in notranjo stran reber. Pri plevritisu dihanje povzroča močne bolečine. Če ga ne zdravimo takoj, se lahko razvije plevralni izliv, pri katerem se v prostoru med obema plastema membrane - imenovanem plevralni prostor - nabira tekočina.
Video vsebina: splošno o plevritisu

Plevritis in plevralni izliv pravzaprav nista bolezni, ampak sta zapleta okužb ali bolezni pljuč, kot so pljučnica, tuberkuloza ali sistemski eritematozni lupus. Plevro razdražijo tudi številna druga stanja - najpogosteje kongestivno srčno popuščanje, lahko pa tudi poškodbe prsnega koša, virusne okužbe, revmatoidni artritis in rak.
Plevritis in plevralni izliv sta ponavadi tako resna, kot je bolezen, ki ju povzroča. Če imate katerega od zgornjih stanj, vas morda že zdravijo zaradi njega; če ne, takoj poiščite zdravniško pomoč.
VZROKI
Dvoplastna plevra ščiti in vlaži površino pljuč, ko se napihujejo in praznijo znotraj prsnega koša. Normalno obe plasti plevre nežno drsita druga ob drugi zaradi tankega, s tekočino napolnjenega prostora - plevralnega prostora - med njima. Če se zaradi okužbe v prsnem košu vnameta, se pri vsakem dihu, kihanju ali kašlju njuni neravni površini drgneta druga ob drugo in povzročata bolečine. To stanje poznamo kot plevritis.
Pri plevritisu se včasih v plevralnem prostoru nabira tekočina, nastane plevralni izliv. Nabiranje tekočine navlaži površino in zmanjša trenje med plastema plevre ter s tem bolečino, ki je povezana s plevritisom, olajša. Hkrati pa tekočina pritiska na pljuča, zmanjšuje njihovo sposobnost raztezanja in povzroča težko dihanje. Tekočina se lahko okuži in nastane stanje, ki ga imenujemo empiem.
DIAGNOSTIČNI POSTOPKI
Za diagnozo plevritisa zdravnik s stetoskopom posluša prsni koš med dihanjem. Če pri tem odkrije plevralno trenje - strgajoč zvok zaradi drgnjenja plasti plevre med seboj - je diagnoza jasna. Plevralno trenje je praskajoč, hreščeč zvok ob koncu vdiha in v začetku izdiha točno nad predelom vnetja plevre. Ob nežnem pretrkavanju tega dela prsnega koša lahko zdravnik sliši prasketanje, še en znak plevritisa.
Zdravnik lahko opravi rentgensko slikanje tega predela in odvzame vzorec plevralne tekočine za analizo. Najprej pod kožo hrbta ali prsnega koša vbrizga anestetik, nato z brizgo izčrpa tekočino. V vzorcu opravi preiskave, s katerimi lahko ugotovi, ali je vzrok nabiranja tekočine rak.
ZDRAVLJENJE
Konvencionalna medicina zdravi bolezni, ki povzročajo plevritis in plevralni izliv.
Video vsebina: Pleuritis - vzroki, diagnoza, simptomi in zdravljenje

Pri plevralnem izlivu je treba včasih poleg tega odstraniti tekočino. Alternativni načini zdravljenja lahko pomagajo olajšati nekatere težave.
KONVENCIONALNA MEDICINA
Poleg antibiotikov in drugih ustreznih zdravil za zdravljenje osnovne bolezni vam bo zdravnik za izboljšanje vnetja predpisal protivnetna zdravila ali analgetike, kot je acetilsalicilna kislina. Za umiritev zelo motečega kašlja včasih predpiše sirup proti kašlju na osnovi kodeina.
Pri plevralnem izlivu zdravniki predlagajo diuretike, ki izločajo odvečno tekočino. Predpišejo lahko tudi antibiotike kot preventivni ukrep proti nastanku emplema. Če je količina plevralne tekočine velika, jo drenirajo skozi cevko, vstavljeno v prsni koš; za ta postopek vas morajo sprejeti v bolnišnico.
ALTERNATIVNI NAČINI
Ozdravitev plevritisa in plevralnega izliva je možna le s konvencionalnim zdravljenjem osnovne bolezni. Številna alternativna zdravljenja, mdr. akupunktura, pa lahko olajšajo nekatere težave, povezane z njima.
PLEVRITIS
Poškodba ali vnetje pljuč lahko povzročita vnetje plevre, tanke dvoplastne opne, ki obdaja pljuča in notranjo stran prsnega koša. Med plastema plevre je s tekočino napolnjen prostor, ki normalno med dihanjem blaži dotikanje med njima. Če je plevra vneta, postaneta površini neravni in občutljivi; med dihanjem se drgneta druga ob drugo in povzročata bolečino.
KITAJSKA ZELIŠČA
Kitajsko zelišče efedra (Ephedra sinica) je močan bronhodilatator in lahko olajša dihanje.
OPOZORILO: Velik odmerek kafre ima enak učinek kot velik odmerek adrenalina; ne uporabljajte je, če imate visok krvni tlak ali srčne bolezni. Pripravite si izvleček tako, da kombinirate 5 g kafre, 4 g vejic cimeta (Cinnamomum cassia), 1,5 g uralskega sladkega korena (Glycyrrhiza uralensis) in 5 g mareličnih koščic (Prunus armeniaca). Mešanico namakajte v hladni vodi nekaj minut, nato jo segrejte do vretja. Pijte vročo.
Vprašanja in odgovori
Kaj je glavni vzrok nastanka pljučnice?
Virusi, ki okužijo vaša pljuča in dihalne poti, lahko povzročijo pljučnico. Gripa (virus gripe) in prehlad (rinovirus) sta najpogostejša vzroka virusne pljučnice pri odraslih. Respiratorni sincicijski virus (RSV) je najpogostejši povzročitelj virusne pljučnice pri majhnih otrocih.
Kateri so simptomi pljučnice?
Simptomi pljučnice:
kašelj – ki je lahko suh ali proizvaja gosto rumeno, zeleno, rjavo ali s krvjo obarvano sluz
oteženo dihanje – vaše dihanje je lahko hitro in plitvo in morda se boste počutili, kot da ste brez zraka
hiter srčni utrip
visoka temperatura
splošno slabo počutje
potenje in drgetanje [1].
Kako resna je lahko pljučnica?
Večina ljudi s pljučnico se dobro odzove na zdravljenje, vendar je pljučnica lahko zelo resna in celo smrtonosna. Verjetnost za zaplete je večja, če ste starejša odrasla oseba, zelo majhen otrok, imate oslabljen imunski sistem ali imate resne zdravstvene težave, kot sta sladkorna bolezen ali ciroza [2].
Koliko dni lahko traja pljučnica?
1. teden – visoka temperatura bi morala izginiti.
4. teden – bolečina v prsnem košu in nastajanje sluzi bi se morala bistveno zmanjšati.
6. teden – kašelj in zasoplost bi se morala bistveno zmanjšati.
3. mesec – večina simptomov bi morala izginiti, vendar se lahko še vedno počutite zelo utrujeni (utrujenost)
Kako se okužiš s pljučnico?
Pljučnica se večinoma širi, ko okuženi ljudje kašljajo, kihajo ali govorijo, pri čemer v zrak pošiljajookužene kapljice. Te kapljice lahko nato vdihnete s tesnim stikom. Manj pogosto lahko dobite pljučnico, če se dotaknete predmeta ali površine, na kateri je mikrob, in se nato dotaknete nosu ali ust.
Kako se pozdravi pljučnico?
Če je vaša pljučnica tako huda, da se zdravite v bolnišnici, vam bodo morda dali intravenske tekočine in antibiotike, pa tudi zdravljenje s kisikom in morda druge načine zdravljenja dihanja.
Ali hoja pomaga pri pljučnici?
Študija razširja izsledke prejšnjih raziskav o učinkih vadbe na pljučnico, tako da dokazuje, da že samo dnevna hoja zadostuje za zmanjšanje s pljučnico povezane umrljivosti med starejšimi ljudmi, ki se redno ne ukvarjajo z drugimi vadbenimi aktivnosti.
Koliko časa traja, da se pljuča zacelijo po pljučnici?
Pljučnica je resna bolezen, ki lahko močno vpliva na človekova pljuča in telo. Traja lahko od enega tedna do več mesecev, da si popolnoma opomoremo," pravi dr. Rayman Lee, pulmolog iz Houstonske bolnišnice.
Kateri so prvi znaki pljučnega raka?
Glavni simptomi pljučnega raka vključujejo:
- kašelj, ki ne izgine po 3 tednih.
- dolgotrajen kašelj, ki se še slabša.
- okužbe prsnega koša, ki se vedno znova vračajo.
- izkašljevanje krvi.
- bolečina pri dihanju ali kašljanju.
- vztrajna zasoplost.
- dolgotrajna utrujenost ali pomanjkanje energije.
Ali se pljučni rak hitro širi?
Pljučni rak je agresivna oblika raka, ki se hitro širi. Stopnje preživetja se sicer izboljšujejo, vendar ostajajo nizke, zlasti pri SCLC tipu pljučnega raka. Zgodnja diagnoza in zdravljenje izboljšata možnosti, da bo oseba živela 5 let ali dlje s pljučnim rakom.
Ali je pljučnega raka mogoče pozdraviti?
Presejalni testi lahko pravočasno identificirajo pljučnega raka.
Pri bolnikih z majhnim pljučnim rakom v zgodnji fazi je lahko stopnja ozdravitve kar 80 do 90-odstotna. Stopnja ozdravitve dramatično upade, ko tumor napreduje in se razširi na bezgavke ali druge dele telesa.
Kje se večinoma pljučni rak prične?
Pljučni rak se običajno aktivira v celicah, ki obdajajo bronhije in dele pljuč, kot so bronhioli ali alveoli. Tanka obloga, imenovana poprsnica, obdaja pljuča. Plevra ščiti vaša pljuča in jim pomaga pri drsenju naprej in nazaj ob steno prsnega koša, ko se med dihanjem širijo in krčijo[3].
Viri in reference
Vir: Družinski zdravstveni vodnik. Konvencionalno in alternativno zdravljenje, Dr. Jajo Lajovic, Založba Mladinska knjiga
1. Pneumonia - Causes and Risk Factors - https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/
2. Pneumonia - https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org
3. What Is Lung Cancer? - https://www.cancer.org/





 Facebook
Facebook
 Instagram
Instagram
 info@moja-lekarna.com
info@moja-lekarna.com

